Sialylated Autoantigen-Reactive IgG Antibodies Attenuate Disease Development in Autoimmune Mouse Models of Lupus Nephritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 29928274
- PMCID: PMC5997785
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01183
Sialylated Autoantigen-Reactive IgG Antibodies Attenuate Disease Development in Autoimmune Mouse Models of Lupus Nephritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
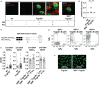
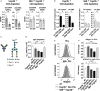
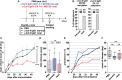
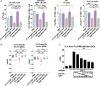
Pro- and anti-inflammatory effector functions of IgG antibodies (Abs) depend on their subclass and Fc glycosylation pattern. Accumulation of non-galactosylated (agalactosylated; G0) IgG Abs in the serum of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients reflects severity of the diseases. In contrast, sialylated IgG Abs are responsible for anti-inflammatory effects of the intravenous immunoglobulin (pooled human serum IgG from healthy donors), administered in high doses (2 g/kg) to treat autoimmune patients. However, whether low amounts of sialylated autoantigen-reactive IgG Abs can also inhibit autoimmune diseases is hardly investigated. Here, we explore whether sialylated autoantigen-reactive IgG Abs can inhibit autoimmune pathology in different mouse models. We found that sialylated IgG auto-Abs fail to induce inflammation and lupus nephritis in a B cell receptor (BCR) transgenic lupus model, but instead are associated with lower frequencies of pathogenic Th1, Th17 and B cell responses. In accordance, the transfer of small amounts of immune complexes containing sialylated IgG Abs was sufficient to attenuate the development of nephritis. We further showed that administration of sialylated collagen type II (Col II)-specific IgG Abs attenuated the disease symptoms in a model of Col II-induced arthritis and reduced pathogenic Th17 cell and autoantigen-specific IgG Ab responses. We conclude that sialylated autoantigen-specific IgG Abs may represent a promising tool for treating pathogenic T and B cell immune responses in autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: IgG glycosylation; ST6gal1; Th17; autoimmunity; immunosuppression; rheumatoid arthritis; sialylation; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The carbohydrate switch between pathogenic and immunosuppressive antigen-specific antibodies.Exp Dermatol. 2013 Aug;22(8):511-4. doi: 10.1111/exd.12171. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Exp Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23808883 Review.
-
T cell-independent B cell activation induces immunosuppressive sialylated IgG antibodies.J Clin Invest. 2013 Sep;123(9):3788-96. doi: 10.1172/JCI65938. Epub 2013 Aug 27. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23979161 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cellular basis for pathogenicity of autoantibodies: lessons from murine monoclonal autoantibodies.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006 Oct;28(2):175-84. doi: 10.1007/s00281-006-0037-0. Epub 2006 Sep 5. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006. PMID: 16953439 Review.
-
Anti-rhesus D prophylaxis in pregnant women is based on sialylated IgG antibodies.F1000Res. 2013 Aug 9;2:169. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.2-169.v1. eCollection 2013. F1000Res. 2013. PMID: 24358898 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin, a non-mutagenic dietary flavonoid, suppresses lupus by inhibiting autoantigen presentation for expansion of autoreactive Th1 and Th17 cells.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(2):R59. doi: 10.1186/ar2682. Epub 2009 Apr 30. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19405952 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Understanding the role of antibody glycosylation through the lens of severe viral and bacterial diseases.Glycobiology. 2020 Mar 20;30(4):241-253. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwaa018. Glycobiology. 2020. PMID: 32103252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profiling the Bisecting N-acetylglucosamine Modification in Amniotic Membrane via Mass Spectrometry.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2022 Aug;20(4):648-656. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2021.09.010. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35123071 Free PMC article.
-
IgG Fc Glycosylation Patterns of Preterm Infants Differ With Gestational Age.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 18;9:3166. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03166. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30713537 Free PMC article.
-
Sialylated immunoglobulin G: a promising diagnostic and therapeutic strategy for autoimmune diseases.Theranostics. 2021 Mar 13;11(11):5430-5446. doi: 10.7150/thno.53961. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33859756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tertiary lymphoid structures as local perpetuators of organ-specific immune injury: implication for lupus nephritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 31;14:1204777. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1204777. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022566 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parekh RB, Roitt IM, Isenberg DA, Dwek RA, Ansell BM, Rademacher TW. Galactosylation of IgG associated oligosaccharides: reduction in patients with adult and juvenile onset rheumatoid arthritis and relation to disease activity. Lancet (1988) 1(8592):966–9.10.1016/S0140-6736(88)91781-3 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

