Gestational Hypothyroxinemia Affects Its Offspring With a Reduced Suppressive Capacity Impairing the Outcome of the Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 29928277
- PMCID: PMC5997919
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01257
Gestational Hypothyroxinemia Affects Its Offspring With a Reduced Suppressive Capacity Impairing the Outcome of the Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Abstract
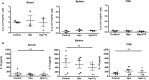
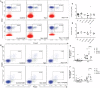
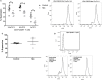
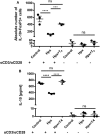
Hypothyroxinemia (Hpx) is a thyroid hormone deficiency (THD) condition highly frequent during pregnancy, which although asymptomatic for the mother, it can impair the cognitive function of the offspring. Previous studies have shown that maternal hypothyroidism increases the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an autoimmune disease model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Here, we analyzed the immune response after EAE induction in the adult offspring gestated in Hpx. Mice gestated in Hpx showed an early appearance of EAE symptoms and the increase of all parameters of the disease such as: the pathological score, spinal cord demyelination, and immune cell infiltration in comparison to the adult offspring gestated in euthyroidism. Isolated CD4+CD25+ T cells from spleen of the offspring gestated in Hpx that suffer EAE showed reduced capacity to suppress proliferation of effector T cells (TEff) after being stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies. Moreover, adoptive transfer experiments of CD4+CD25+ T cells from the offspring gestated in Hpx suffering EAE to mice that were induced with EAE showed that the receptor mice suffer more intense EAE pathological score. Even though, no significant differences were detected in the frequency of Treg cells and IL-10 content in the blood, spleen, and brain between mice gestated in Hpx or euthyroidism, T cells CD4+CD25+ from spleen have reduced capacity to differentiate in vitro to Treg and to produce IL-10. Thus, our data support the notion that maternal Hpx can imprint the immune response of the offspring suffering EAE probably due to a reduced capacity to trigger suppression. Such "imprints" on the immune system could contribute to explaining as to why adult offspring gestated in Hpx suffer earlier and more intense EAE.
Keywords: T regulatory cells; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; hypothyroxinemia; multiple sclerosis; pregnancy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gestational Hypothyroxinemia Imprints a Switch in the Capacity of Astrocytes and Microglial Cells of the Offspring to React in Inflammation.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 May;55(5):4373-4387. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0627-y. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28656482
-
Gestational Hypothyroxinemia Shifts Th1/Th17 Immunity and Innate Lymphoid Cell Balance in the Adult Offspring during the Presymptomatic Stage of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2025;32(1):126-138. doi: 10.1159/000545578. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2025. PMID: 40209697
-
Gestational hypothyroidism increases the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in adult offspring.Thyroid. 2013 Dec;23(12):1627-37. doi: 10.1089/thy.2012.0401. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Thyroid. 2013. PMID: 23777566 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinting of maternal thyroid hormones in the offspring.Int Rev Immunol. 2017 Jul 4;36(4):240-255. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2016.1277216. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Int Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28272924 Review.
-
Th9 cells in the pathogenesis of EAE and multiple sclerosis.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Jan;39(1):79-87. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0604-y. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 27844107 Review.
Cited by
-
Parental Uveitis Influences Offspring With an Increased Susceptibility to the Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 16;11:1053. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01053. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32612602 Free PMC article.
-
Female offspring gestated in hypothyroxinemia and infected with human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) suffer a more severe infection and have a higher number of activated CD8+ T lymphocytes.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 8;13:966917. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.966917. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36159799 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota short-chain fatty acids and their impact on the host thyroid function and diseases.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 30;14:1192216. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1192216. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37455925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk Factors from Pregnancy to Adulthood in Multiple Sclerosis Outcome.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 25;23(13):7080. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137080. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gestational hypothyroxinemia induces ASD-like phenotypes in behavior, proinflammatory markers, and glutamatergic protein expression in mouse offspring of both sexes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 May 1;15:1381180. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1381180. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38752179 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

