MicroRNA-216b regulated proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting SOX9
- PMID: 29928377
- PMCID: PMC6004665
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8573
MicroRNA-216b regulated proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting SOX9
Abstract
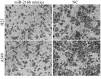
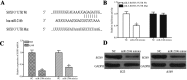
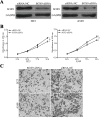
Micro (mi)RNAs are small, evolutionarily conserved and endogenous noncoding RNA molecules between 19 and 24 nucleotides in length. The potential roles of miRNAs in the carcinogenesis and progression of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have been studied previously. In the present study, it was revealed that miRNA-216b (miR-216b) expression was lower in NSCLC tissue and cell lines compared with that in adjacent healthy lung tissue samples and the normal bronchial epithelial 16HBE cell line, respectively. The ectopic expression of miR-216b inhibited the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells in vitro. SRY-Box 9 (SOX9) was identified as a direct target of miR-216b in NSCLC. In addition, SOX9 small interfering RNA was able to mimic the effects of miR-216b overexpression on cell proliferation and invasion in NSCLC. Therefore, the data reported in the present study demonstrate that miR-216b is an important tumor suppressor in NSCLC. These data may contribute to the understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying the carcinogenesis and progression of NSCLC, and provide novel therapies for patients with NSCLC.
Keywords: SRY-Box 9; invasion; microRNA-216b; non-small-cell lung cancer; proliferation.
Figures
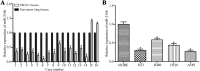

Similar articles
-
MiR-216b suppresses cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating FOXM1 expression in human non-small cell lung cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Apr 18;12:2999-3009. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S202523. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31114243 Free PMC article.
-
The PVT1/miR-216b/Beclin-1 regulates cisplatin sensitivity of NSCLC cells via modulating autophagy and apoptosis.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019 May;83(5):921-931. doi: 10.1007/s00280-019-03808-3. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30859368
-
Overexpression of miR-216b sensitizes NSCLC cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by targeting c-Jun.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 27;8(61):104206-104215. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22171. eCollection 2017 Nov 28. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29262633 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-216b reduces growth, migration and invasion of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells by directly targeting ρ-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1.Oncol Lett. 2018 May;15(5):6745-6751. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8109. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Oncol Lett. 2018. Retraction in: Oncol Lett. 2022 Jun 06;24(2):243. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13363. PMID: 29616134 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
MiR-216b inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting Forkhead Box M1.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):5435-5443. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27822. Epub 2018 Oct 9. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30302807
Cited by
-
MiR-216b suppresses cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating FOXM1 expression in human non-small cell lung cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Apr 18;12:2999-3009. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S202523. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31114243 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑203a‑3p is a candidate tumor suppressor that targets thrombospondin 2 in colorectal carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2019 Nov;42(5):1825-1832. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7310. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31545460 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of miRNA-216b is negatively correlated with 18F-FDG uptake in non-small cell lung cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Sep 1;19(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02376-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34470640 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-5195-3p mediated malignant biological behaviour of insulin-resistant liver cancer cells via SOX9 and TPM4.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 16;23(1):557. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11068-x. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37328795 Free PMC article.
-
Thiostrepton and miR-216b synergistically promote osteosarcoma cell cytotoxicity and apoptosis by targeting FoxM1.Oncol Lett. 2020 Dec;20(6):391. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12254. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 33193851 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
