The Effect of Workplace Bullying Perception on Psychological Symptoms: A Structural Equation Approach
- PMID: 29928536
- PMCID: PMC6005929
- DOI: 10.1016/j.shaw.2017.06.010
The Effect of Workplace Bullying Perception on Psychological Symptoms: A Structural Equation Approach
Abstract
Background: The aims of this study were to determine the extent of workplace bullying perceptions among the employees of a Faculty of Medicine, evaluating the variables considered to be associated, and determining the effect of workplace bullying perceptions on their psychological symptoms evaluated by the Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI).
Methods: This cross-sectional study was performed involving 355 (88.75%) employees.
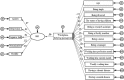
Results: Levels of perceived workplace bullying were found to increase with the increasing scores for BSI and BSI sub-dimensions of anxiety, depression, negative self, somatization, and hostility (all p < 0.001). One point increase in the workplace bullying perception score was associated with a 0.47 point increase in psychological symptoms evaluated by BSI. Moreover, the workplace bullying perception scores were most strongly affected by the scores of anxiety, negative self, depression, hostility, and somatization (all p < 0.05).
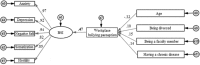
Conclusion: The present results revealed that young individuals, divorced individuals, faculty members, and individuals with a chronic disease had the greatest workplace bullying perceptions with our study population. Additionally, the BSI, anxiety, depression, negative self, somatization, and hostility scores of the individuals with high levels of workplace bullying perceptions were also high.
Keywords: negative acts questionnaire; psychological symptoms; workplace bullying.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO; Geneva (Switzerland): 2002. World report on violence and health: Summary.http://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/violence/worldreport/en/su... Available from:
-
- Kırel Ç. vol. 206. Anadolu Üniversitesi İktisadi ve İdari Bilimler Fakültesi Yayınları; 2008. (Örgütlerde psikolojik taciz (mobbing) ve yönetimi).
-
- International Council of Nurses (ICN), Public Services International (PSI), World Health Organization (WHO), International Labour Organization (ILO) ICN, PSI, WHO, ILO; Geneva (Switzerland): 2005. Framework guidelines for addressing workplace violence in the health sector, the training manual.http://www.ilo.org/safework/info/instr/WCMS_108542/lang–en/index.htm Available from:
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) American Psychiatric Association; Washington, D. C.: 2013. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. Vol. 5th ed.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) 1993. The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders: diagnostic criteria for research. Geneva.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

