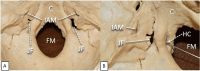
Cranial Nerve Foramina: Part II - A Review of the Anatomy and Pathology of Cranial Nerve Foramina of the Posterior Cranial Fossa
- PMID: 29928560
- PMCID: PMC6005399
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2500
Cranial Nerve Foramina: Part II - A Review of the Anatomy and Pathology of Cranial Nerve Foramina of the Posterior Cranial Fossa
Abstract
Cranial nerve foramina are integral exits from the confines of the skull. Despite their significance in cranial nerve pathologies, there has been no comprehensive anatomical review of these structures. Owing to the extensive nature of this topic we have divided our review into two parts; Part II, presented here, focuses on the foramina of the posterior cranial fossa and discusses each foramen's shape, orientation, size, surrounding structures, and structures that pass through it. Furthermore, by comparing foramen sizes against the cross-sectional areas of their contents, we determine the amount of free space available within each. We also review lesions that can obstruct each foramen and discuss the clinical consequences.
Keywords: cranial nerve; foramen; foramen magnum; hypoglossal canal; internal acoustic meatus; jugular foramen; posterior fossa; skull base.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cranial Nerve Foramina Part I: A Review of the Anatomy and Pathology of Cranial Nerve Foramina of the Anterior and Middle Fossa.Cureus. 2018 Feb 8;10(2):e2172. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2172. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 29644159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variant Bilateral Foramina of the Middle Cranial Fossa.Cureus. 2022 Dec 27;14(12):e33014. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33014. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36712744 Free PMC article.
-
Endonasal access to lower cranial nerves: From foramina to upper parapharyngeal space.Head Neck. 2021 Oct;43(10):3225-3233. doi: 10.1002/hed.26781. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Head Neck. 2021. PMID: 34165854
-
Visualization of Dark Side of Skull Base with Surgical Navigation and Endoscopic Assistance: Extended Petrous Rhomboid and Rhomboid with Maxillary Nerve-Mandibular Nerve Vidian Corridor.World Neurosurg. 2019 Sep;129:e134-e145. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.05.062. Epub 2019 May 17. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31103769
-
The variable relationship between the lower cranial nerves and jugular foramen tumors: implications for neural preservation.Am J Otol. 1996 Jul;17(4):658-68. Am J Otol. 1996. PMID: 8841718 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomechanical analysis of skull trauma and opportunity in neuroradiology interpretation to explain the post-concussion syndrome: literature review and case studies presentation.Eur Radiol Exp. 2020 Dec 8;4(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s41747-020-00194-x. Eur Radiol Exp. 2020. PMID: 33289040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lower cranial nerve syndromes: a review.Neurosurg Rev. 2021 Jun;44(3):1345-1355. doi: 10.1007/s10143-020-01344-w. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Neurosurg Rev. 2021. PMID: 32638140 Review.
-
Case report: A rare case of neurocytoma of the Vth cranial nerve.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 27;14:1438011. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1438011. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39399175 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclast activity sculpts craniofacial form to permit sensorineural patterning in the zebrafish skull.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 1;13:969481. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.969481. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36387889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foramen magnum, occipital condyles and hypoglossal canals morphometry: anatomical study with clinical implications. Lyrtzis CH, Piagkou M, Gkioka A, Anastasopoulos N, Apostolidis S, Natsis K. Folia Morphol. 2017;76:446–457. - PubMed
-
- Netter F. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2011. Atlas of Human Anatomy.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources