Imaging of Sodium MRI for Therapy Evaluation of Brain Metastase with Cyberknife at 7T: A Case Report
- PMID: 29928562
- PMCID: PMC6005396
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2502
Imaging of Sodium MRI for Therapy Evaluation of Brain Metastase with Cyberknife at 7T: A Case Report
Abstract
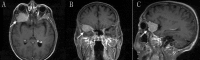
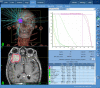
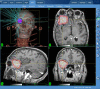
Herein we describe the case of an elderly patient who presented with a recent history of impaired vision of the right eye around three months due to brain lesions. He was diagnosed with liver cancer and underwent surgery three months prior. The pathological result is hepatocellular carcinoma. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed the diagnosis of brain to be metastatic. The patient selected CyberKnife (Accuray Incorporated, Sunnyvale, USA) radiosurgery for the brain lesion since his physical conditions are not suitable for craniotomy. We adapt the imaging of sodium MRI and proton diffusion mapping at 7T MR system to evaluate the efficacy following CyberKnife early stage treatment. To date, we find the tissue sodium concentration (TSC) changes with the time whereas the proton MRI has no significant change within one month. The time course of sodium concentration in the tumor showed a dramatic increase in the treated brain tumor compared to the pretreatment sodium concentration and 48 hours after stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), which is correlated to the period of the radiotherapy-induced cellular necrosis. This case demonstrates the possibility of sodium MRI as a biomarker for monitoring early radiotherapy for assessing tumor cellularity.
Keywords: brain metastase; cyberknife; sodium mri; tissue sodium concentration (tsc).
Conflict of interest statement
We want to know if the co-author Zihao Zhang could be listed as co-first author?
Figures


References
-
- Understanding the sodium pump and its relevance to disease. Rose AM, Valdes R. http://clinchem.aaccjnls.org/content/40/9/1674.long. Clin Chem. 1994;40:1674–1685. - PubMed
-
- Loss of cell ion homeostasis and cell viability in the brain: what sodium MRI can tell us. Boada FE, LaVerde G, Jungreis C, et al. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2005;70:77–101. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
