In-host modeling
- PMID: 29928736
- PMCID: PMC6001971
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idm.2017.04.002
In-host modeling
Abstract
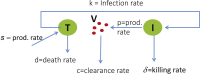
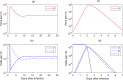
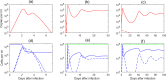
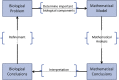
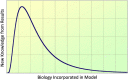
Understanding the mechanisms governing host-pathogen kinetics is important and can guide human interventions. In-host mathematical models, together with biological data, have been used in this endeavor. In this review, we present basic models used to describe acute and chronic pathogenic infections. We highlight the power of model predictions, the role of drug therapy, and advantage of considering the dynamics of immune responses. We also present the limitations of these models due in part to the trade-off between the complexity of the model and their predictive power, and the challenges a modeler faces in determining the appropriate formulation for a given problem.
Figures
References
-
- Arinaminpathy N., Metcalf C.J.E., Grenfell B.T. Springer; 2014. Viral dynamics and mathematical models. In viral infections of humans.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

