Higher levels of thyroxine may predict a favorable response to donepezil treatment in patients with Alzheimer disease: a prospective, case-control study
- PMID: 29929471
- PMCID: PMC6013955
- DOI: 10.1186/s12868-018-0436-x
Higher levels of thyroxine may predict a favorable response to donepezil treatment in patients with Alzheimer disease: a prospective, case-control study
Abstract
Background: Cholinergic hypothesis has been advanced as an etiology of Alzheimer disease (AD) on the basis of the presynaptic deficit found in the diseased brains, and cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs) are the treatment of choice for these patients. However, only about half of treatment efficacy was found. Because increasing evidence supports an extensive interrelationship between thyroid hormones (THs), cortisol level and the cholinergic system, the aim of the present study was to evaluate thyroid function and cortisol level in patients with mild to moderate AD before and after ChEIs treatment, and to identify possible variations in response. This was a prospective, case-control, follow-up study. Levels of cortisol and THs were evaluated in 21 outpatients with mild to moderate AD and 20 normal controls. All patients were treated with 5 mg/day of donepezil (DPZ) and were reevaluated after 24-26 weeks of treatment.
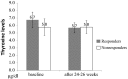
Results: The patients had worse cognitive function, higher cortisol level, and lower levels of triiodothyronine (T3) and its free fraction than the controls. There were no significant differences in global cognitive function or cortisol level after treatment, however, significant reductions in T3 and thyroxin (T4) levels were observed. Responders had higher levels of T4 than non-responders, followed by a significant reduction after treatment.
Conclusions: These results suggest that relatively higher levels of T4 may predict a favorable response to DPZ treatment. Further studies are warranted to confirm the relationship between THs and ChEIs therapy in AD and to explore new therapeutic strategies. On the other hand, cortisol levels are more likely to respond to interventions for stress-related neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with AD rather than ChEIs treatment. Further studies are warranted to investigate the association between cortisol level and the severity of stress-related neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; Cholinesterase inhibitors; Cortisol; Donepezil; Thyroid hormone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thyroid function in patients with Alzheimer disease: implications on response to anticholinesterase treatment.Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2006 Oct-Dec;20(4):242-7. doi: 10.1097/01.wad.0000213856.89613.59. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2006. PMID: 17132968
-
Sex influences on cholinesterase inhibitor treatment in elderly individuals with Alzheimer's disease.Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2006 Sep;4(3):273-86. doi: 10.1016/j.amjopharm.2006.09.009. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 17062329 Review.
-
Distinctive Effect of Donepezil Treatment on P300 and N200 Subcomponents of Auditory Event-Related Evoked Potentials in Alzheimer Disease Patients.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Jul 3;21:1920-7. doi: 10.12659/MSM.894940. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26138001 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid function in patients with Alzheimer's disease treated with cholinesterase inhibitors.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2003;63(4):389-92. doi: 10.55782/ane-2003-1479. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2003. PMID: 15053263
-
Pharmacology and clinical efficacy of cholinesterase inhibitors.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1998 Nov 1;55 Suppl 2:S22-5. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/55.suppl_2.S22. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1998. PMID: 9809108 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between thyroid function and Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Oct;36(7):1523-1543. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00760-1. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 34146214
-
Advances in the Study of the Pathology and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease and Its Association with Periodontitis.Life (Basel). 2023 Nov 13;13(11):2203. doi: 10.3390/life13112203. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between cortisol, Interleukin-6 and homocysteine in Alzheimer's disease.Qatar Med J. 2021 Sep 6;2021(33):1-10. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2021.33. eCollection 2021. Qatar Med J. 2021. PMID: 34604020 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of response to acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in dementia: A systematic review.Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 20;16:998224. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.998224. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36203811 Free PMC article.
-
The disturbance of thyroid-associated hormone and its receptors in brain and blood circulation existed in the early stage of mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Mar 7;15(5):1591-1602. doi: 10.18632/aging.204570. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 36897166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayashi M, Patel AJ. An interaction between thyroid hormone and nerve growth factor in the regulation of choline acetyltranserase activity in neuronal cultures derived from the septal-diagonal band region of the embryonic rat brain. Brain Res. 1987;36:109–120. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90069-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

