CFTR is required for the migration of primordial germ cells during zebrafish early embryogenesis
- PMID: 29930176
- PMCID: PMC6106808
- DOI: 10.1530/REP-17-0681
CFTR is required for the migration of primordial germ cells during zebrafish early embryogenesis
Abstract
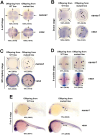
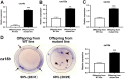
Mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene affect fertility in both sexes. However, the involvement of CFTR in regulating germ cell development remains largely unknown. Here, we used zebrafish model to investigate the role of CFTR in primordial germ cells (PGCs) development. We generated a cftr frameshift mutant zebrafish line using CRISPR/Cas9 technique and investigated the migration of PGCs during early embryo development. Our results showed that loss of Cftr impairs the migration of PGCs from dome stages onward. The migration of PGCs was also perturbed by treatment of CFTRinh-172, a gating-specific CFTR channel inhibitor. Moreover, defected PGCs migration in cftr mutant embryos can be partially rescued by injection of WT but not other channel-defective mutant cftr mRNAs. Finally, we observed the elevation of cxcr4b, cxcl12a, rgs14a and ca15b, key factors involved in zebrafish PGCs migration, in cftr-mutant zebrafish embryos. Taken together, the present study revealed an important role of CFTR acting as an ion channel in regulating PGCs migration during early embryogenesis. Defect of which may impair germ cell development through elevation of key factors involved in cell motility and response to chemotactic gradient in PGCs.
© 2018 The authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures



References
-
- Chen H, Guo JH, Lu YC, Ding GL, Yu MK, Tsang LL, Fok KL, Liu XM, Zhang XH, Chung YW. et al. 2012. Impaired CFTR-dependent amplification of FSH-stimulated estrogen production in cystic fibrosis and PCOS. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 97 923–932. (10.1210/jc.2011-1363) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

