Accidental aspiration of a solid tablet of sodium hydroxide
- PMID: 29930183
- PMCID: PMC6020962
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224213
Accidental aspiration of a solid tablet of sodium hydroxide
Erratum in
-
Correction: Accidental aspiration of a solid tablet of sodium hydroxide.BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Aug 17;2018:bcr2018224213corr1. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224213corr1. BMJ Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30121563 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
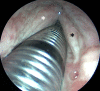
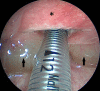
Sodium hydroxide is a corrosive, highly alkaline (PKa=14.8) household product. Ingestion of sodium hydroxide liquid is common, showing toxicity on the oesophagus and stomach. Nevertheless, cases of sodium hydroxide ingestions in pellet are rare and the management of them is unknown. We report the case of a 65-year-old man who accidentally swallowed a bleach tablet of 3.5 g. Six hours later, the patient developed an aphonia associated with dysponea stage IV, motivating a nasofibroscopy showing glottis and supraglottic necrosis and oedema for which the patient received intravenous steroids, was intubated and then underwent a tracheotomy. After 2 weeks under tracheotomy, local evolution was favourable allowing a removal of the cannula and a return back home.
Keywords: ear, nose and throat/otolaryngology; poisoning; resuscitation.
© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
