Tuning the Cytokine Responses: An Update on Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 Receptor Complexes
- PMID: 29930549
- PMCID: PMC6001902
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00888
Tuning the Cytokine Responses: An Update on Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 Receptor Complexes
Abstract
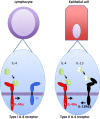
Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 are related cytokines that regulate many aspects of allergic inflammation. They play important roles in regulating the responses of lymphocytes, myeloid cells, and non-hematopoietic cells. In T-cells, IL-4 induces the differentiation of naïve CD4 T cells into Th2 cells, in B cells, IL-4 drives the immunoglobulin (Ig) class switch to IgG1 and IgE, and in macrophages, IL-4 and IL-13 induce alternative macrophage activation. This review gives a short insight into the functional formation of these cytokine receptors. I will discuss both the binding kinetics of ligand/receptor interactions and the expression of the receptor chains for these cytokines in various cell types; both of which are crucial factors in explaining the efficiency by which these cytokines induce intracellular signaling and gene expression. Work initiated in part by William (Bill) E. Paul on IL-4 some 30 years ago has now grown into a major building block of our current understanding of basic immunology and the immune response. This knowledge on IL-4 has growing clinical importance, as therapeutic approaches targeting the cytokine and its signal transduction are becoming a part of the clinical practice in treating allergic diseases. Just by reading the reference list of this short review, one can appreciate the enormous input Bill has had on shaping our understanding of the pathophysiology of allergic inflammation and in particular the role of IL-4 in this process.
Keywords: STAT6; allergic inflammation; cytokine signaling; interleukin-4; interleukin-4 receptor; signal transduction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Targeting of the Interleukin-4/Interleukin-13 Signaling Pathway: In Allergy and Beyond.BioDrugs. 2018 Jun;32(3):201-220. doi: 10.1007/s40259-018-0280-7. BioDrugs. 2018. PMID: 29736903 Review.
-
Roles of IL-4, IL-13, and Their Receptors in Lung Cancer.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2024 Sep;44(9):399-407. doi: 10.1089/jir.2024.0008. Epub 2024 Mar 22. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2024. PMID: 38516928 Review.
-
Commentary: IL-4 and IL-13 receptors and signaling.Cytokine. 2015 Sep;75(1):38-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.023. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 26187331 Free PMC article.
-
Differential requirements for interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 in protein contact dermatitis induced by Anisakis.Allergy. 2009 Sep;64(9):1309-18. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02002.x. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Allergy. 2009. PMID: 19254288
-
Deletion of IL-4Rα signaling on B cells limits hyperresponsiveness depending on antigen load.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021 Jul;148(1):99-109.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.12.635. Epub 2020 Dec 28. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33383090 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Padina Minor Extract Confers Resistance against Candida Albicans Infection: Evaluation in a Zebrafish Model.Biology (Basel). 2024 May 27;13(6):384. doi: 10.3390/biology13060384. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927264 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Pathogenic Role of Protease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 12;24(24):17372. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417372. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Microcirculation, Cytokine Profile, and Local Antioxidant Protection Indices in Periodontal Health, and Stage II, Stage III Periodontitis.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 18;10(6):1262. doi: 10.3390/jcm10061262. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33803774 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of genetically modified Lactococcus lactis that produces bioactive anti-interleukin-4 single-chain fragment variable.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Sep;47(9):7039-7047. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05765-0. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32880064
-
Cellular and microenvironmental cues that promote macrophage fusion and foreign body response.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 5;15:1411872. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1411872. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39034997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol (1986) 136:2348–57. - PubMed
-
- Seder RA, Paul WE, Dvorak AM, Sharkis SJ, Kagey-Sobotka A, Niv Y, et al. Mouse splenic and bone marrow cell populations that express high-affinity Fc epsilon receptors and produce interleukin 4 are highly enriched in basophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1991) 88:2835–9.10.1073/pnas.88.7.2835 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nonaka M, Nonaka R, Woolley K, Adelroth E, Miura K, Okhawara Y, et al. Distinct immunohistochemical localization of IL-4 in human inflamed airway tissues. IL-4 is localized to eosinophils in vivo and is released by peripheral blood eosinophils. J Immunol (1995) 155:3234–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

