Resultados a longo prazo da angioplastia de artérias renais com stent na doença aterosclerótica: revisão sistemática
- PMID: 29930639
- PMCID: PMC5915863
- DOI: 10.1590/1677-5449.010816
Resultados a longo prazo da angioplastia de artérias renais com stent na doença aterosclerótica: revisão sistemática
Abstract
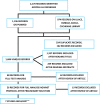
Abstract: Atherosclerotic renovascular disease is the most important cause of secondary hypertension. The natural history of the disease reveals progression rates of 4 to 12% per year. Angioplasty with renal artery stenting is one treatment option; but there are few studies that have reported long-term results. The objective of this systematic literature review is to discuss the long-term results (at least 24 months) of angioplasty with stenting of renal arteries for atherosclerotic disease, in terms of renal function and blood pressure levels for control of hypertension. A thorough search was conducted of LILACS, EMBASE, SCIELO, Cochrane Library, and MEDLINE using the appropriate terms. Just seven out of 2170 references identified met all inclusion criteria. It was concluded that over the long term renal function was stabilized, blood pressure levels were reduced, and the number of classes of antihypertensive medication decreased.
A doença renovascular aterosclerótica é a principal causa de hipertensão secundária. A história natural da doença demonstra taxas de progressão de 4 a 12% ao ano. Entre os métodos de tratamento existe a angioplastia com stent de artérias renais; porém, poucos estudos clínicos demonstraram seus resultados a longo prazo. Esta revisão sistemática da literatura se propõe a apresentar os resultados a longo prazo (acima de 24 meses) da angioplastia com stent de artérias renais na doença aterosclerótica em relação à função renal e aos níveis pressóricos no controle da hipertensão. Foi realizada uma ampla pesquisa, utilizando os termos apropriados, nas bases de dados LILACS, EMBASE, SCIELO, Cochrane Library e MEDLINE. De um total de 2.170 referências, apenas sete artigos contemplavam todos os critérios de inclusão. Conclui-se que, a longo prazo, há uma estabilização da função renal, redução dos níveis pressóricos e diminuição do número de classes de medicamentos anti-hipertensivos.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflito de interesse: Os autores declararam não haver conflitos de interesse que precisam ser informados.
Figures
References
-
- Cooper CJ, Murphy TP, Cutlip DE, et al. Stenting and medical therapy for atherosclerotic renal-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(1):13–22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1310753 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guillaumon AT, Rocha EF, Medeiros CAF. Endovascular treatment of renal stenosis in solitary kidney. J Vasc Bras. 2008;7(2):99–105. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1677-54492008000200003 - DOI
-
- Minuz P, Patrignani P, Gaino S, et al. Increased oxidative stress and platelet activation in patients with hypertension and renovascular disease. Circulation. 2002;106(22):2800–2805. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000039528.49161.E9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuller LH, Shemanski L, Psaty BM, et al. Subclinical disease as an independent risk fa tor for cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 1995;92(4):720–726. http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.92.4.720 - DOI - PubMed
-
- O’Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK., Jr Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(1):14–22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199901073400103 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous