Pseudoaneurisma da artéria temporal superficial: relato de três casos
- PMID: 29930686
- PMCID: PMC5990264
- DOI: 10.1590/1677-5449.009517
Pseudoaneurisma da artéria temporal superficial: relato de três casos
Abstract
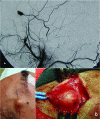
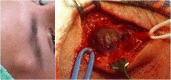
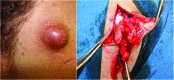
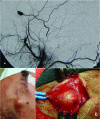
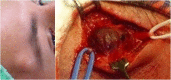
Abstract: Pseudoaneurysms of the superficial temporal artery are rare events. They primarily occur in young men as a consequence of blunt head traumas. The majority of cases are asymptomatic, although there are sometimes vague symptoms. Ruptured pseudoaneurysms and development of neurological deficits are occasional complications. The authors describe three cases of pseudoaneurysm of the superficial temporal artery after blunt head trauma. Patients were successfully managed with ligature and resection of the pseudoaneurysms.
O pseudoaneurisma da artéria temporal superficial é um evento raro. Ocorre principalmente em homens jovens em decorrência de traumatismo craniano fechado. A maioria dos casos é assintomática, podendo eventualmente haver associação com sintomas vagos. A rotura do pseudoaneurisma e o desenvolvimento de déficits neurológicos são complicações esporádicas. Os autores relatam três casos de pseudoaneurisma de artéria temporal superficial pós-traumatismo craniano fechado. Os pacientes foram manejados com sucesso por ligadura e ressecção dos pseudoaneurismas.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflito de interesse: Os autores declararam não haver conflitos de interesse que precisam ser informados.
Figures

References
-
- Peick AL, Nichols WR, Curtis JJ, Silver D. Aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms of the superficial temporal artery caused by trauma. J Vasc Surg. 1988;8(5):606–610. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0741-5214(88)90312-6 - DOI - PubMed
-
- DeSanti L. Des tumeurs aneurysms de la region temporale. Arch Gen Med. 1884;154:543–679.
-
- Brown RK, Mehnert RH. Aneurysm of the temporal artery. Surgery. 1942;12:711–714.
-
- Schechter MM, Gutstein RA. Aneurysms and arteriovenous fistulas of the superficial temporal vessels. Radiology. 1970;97(3):549–557. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/97.3.549 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Winslow N, Edwards M. Aneurysm of the temporal artery. Surgery. 1935;28:696–702.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
