Shape-, size- and structure-controlled synthesis and biocompatibility of iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic theranostics
- PMID: 29930730
- PMCID: PMC6010979
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.25220
Shape-, size- and structure-controlled synthesis and biocompatibility of iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic theranostics
Abstract
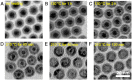
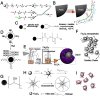
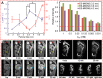
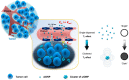
In the past decade, iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) have attracted more and more attention for their excellent physicochemical properties and promising biomedical applications. In this review, we summarize and highlight recent progress in the design, synthesis, biocompatibility evaluation and magnetic theranostic applications of IONPs, with a special focus on cancer treatment. Firstly, we provide an overview of the controlling synthesis strategies for fabricating zero-, one- and three-dimensional IONPs with different shapes, sizes and structures. Then, the in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility evaluation and biotranslocation of IONPs are discussed in relation to their chemo-physical properties including particle size, surface properties, shape and structure. Finally, we also highlight significant achievements in magnetic theranostic applications including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic hyperthermia and targeted drug delivery. This review provides a background on the controlled synthesis, biocompatibility evaluation and applications of IONPs as cancer theranostic agents and an overview of the most up-to-date developments in this area.
Keywords: biocompatibility; controlled synthesis; iron oxide; magnetic theranostics.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
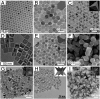
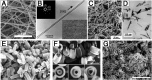

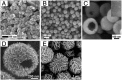
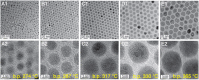





References
-
- Bazylinski DA, Frankel RB. Magnetosome formation in prokaryotes. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:217–230. - PubMed
-
- Diebel CE, Proksch R, Green CR, Neilson P, Walker MM. Magnetite defines a vertebrate magnetoreceptor. Nature. 2000;406:299–302. - PubMed
-
- Liu G, Men P, Harris PLR, Rolston RK, Perry G, Smith MA. Nanoparticle iron chelators: A new therapeutic approach in alzheimer disease and other neurologic disorders associated with trace metal imbalance. Neurosci. Lett. 2006;406:189–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

