Construction and characterization of a new TRAIL soluble form, active at picomolar concentrations
- PMID: 29930761
- PMCID: PMC6007462
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.25519
Construction and characterization of a new TRAIL soluble form, active at picomolar concentrations
Abstract
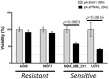
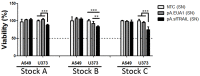
Apoptosis induction has emerged as a treatment option for anticancer therapy. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), a type II transmembrane protein, is a potent and specific pro-apoptotic protein ligand, which activates the extrinsic apoptosis pathway of the cell death receptors. Here we describe the construction and characterization of a new soluble TRAIL, sfTRAIL, stabilized with the trimerization Foldon domain from the Fibritin protein of the bacteriophage T4. Supernatants of 0.22 μM-filtered supernatants were produced in Vero-transduced cells with HSV1-derived viral amplicon vectors. Experiments were undertaken in two known TRAIL-sensitive (U373 and MDA.MB.231) and two TRAIL-resistant (MCF7 and A549) cell lines, to determine (i) whether the sfTRAIL protein is synthetized and, (ii) whether sfTRAIL could induce receptor-mediated apoptosis. Our results showed that sfTRAIL was able to induce apoptosis at concentrations as low as 1899.29 pg/mL (27.71 pM), independently of caspase-9 activation, and reduction in cell viability at 998.73 fM.
Keywords: TRAIL; amplicon vectors; apoptosis; cancer treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Authors MEM and ALC have a patent for this technology.
Figures


References
-
- Savill J, Fadok V. Corpse clearance defines the meaning of cell death. Nature. 2000;407:784–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/35037722. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Holland P, Eckhardt SG. Ligand-based targeting of apoptosis in cancer: the potential of recombinant human apoptosis ligand 2/Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhApo2L/TRAIL) J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3621–30. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.15.7198. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wiezorek J, Holland P, Graves J. Death receptor agonists as a targeted therapy for cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:1701–8. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1692. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holland PM. Death receptor agonist therapies for cancer, which is the right TRAIL? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014;25:185–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.12.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hymowitz SG, O’Connell MP, Ultsch MH, Hurst A, Totpal K, Ashkenazi A, de Vos AM, Kelley RF. A unique zinc-binding site revealed by a high-resolution X-ray structure of homotrimeric Apo2L/TRAIL. Biochemistry. 2000;39:633–40. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi992242l. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

