Efficacy of orlistat in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29930810
- PMCID: PMC6007047
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2018.1100
Efficacy of orlistat in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
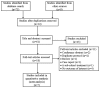
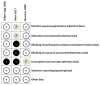
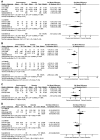
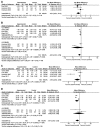
In the present meta-analysis, the efficacy and safety of orlistat in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) were evaluated. PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and Wan Fang data were searched for controlled trials of orlistat in patients with NAFLD or NASH, published before August 2017. Three randomized controlled trials and four single-arm trials were included. The involved participants with NAFLD or NASH (330 patients) were analyzed for clinical outcomes including alteration in hepatic histological variables and biomarkers of liver function. Improvements were observed in levels of alanine aminotransferase [standard mean difference (SMD)=-1.41; P=0.01], aspartate aminotransferase (SMD=-2.06; P=0.0005), γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (SMD=-1.91; P=0.05), glucose [mean difference (MD)=-0.51; P=0.01], triglycerides (MD=-0.93; P=0.01), homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance index (MD=-1.05; P=0.04) and body mass index (MD=-1.97; P=0.02), but not in liver fibrosis score (SMD=-0.14; P=0.71). On sub-analyses of the different patient groups, no significant differences were observed in patients with NASH. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that orlistat could serve as a therapeutic drug to improve biochemical indicators of liver damage, but not as first-choice drug for the management of NAFLD or NASH; thus suggesting a novel palliative drug only for the treatment of NAFLD.
Keywords: meta-analysis; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; orlistat.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
