Evaluation of morphine-like effects of the mixed mu/delta agonist morphine-6- O-sulfate in rats: Drug discrimination and physical dependence
- PMID: 29930811
- PMCID: PMC6009770
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.403
Evaluation of morphine-like effects of the mixed mu/delta agonist morphine-6- O-sulfate in rats: Drug discrimination and physical dependence
Abstract
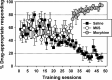
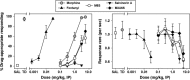
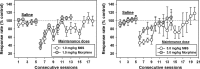
Morphine-6-O-sulfate (M6S) is as a mixed-action mu/delta (μ/δ) opioid receptor agonist with high potency and analgesic efficacy. These studies used assays of drug discrimination and schedule-controlled responding to assess abuse-liability, tolerance, and physical dependence as compared to morphine in rats. Attempts to train 0.3 mg/kg (IP) M6S from saline failed, but all rats rapidly acquired the discrimination when the training dose was changed to 3.0 mg/kg morphine, and substitution tests showed that morphine and fentanyl both fully substituted for the training dose, M6S and M3A6S (3-O-acetyl ester of M6S) only partially substituted, and salvinorin A did not elicit morphine-like effects. Tolerance to response rate-decreasing effects was studied in rats administered either 1.0 or 3.0 mg/kg morphine or M6S before food-reinforced operant sessions. At both unit doses, tolerance to M6S-elicited rate suppression developed more slowly than tolerance to morphine-induced reductions in response rates. To assess dependence, rats were maintained on 1.0 mg/kg morphine or 1.0 mg/kg M6S until food-reinforced response rates were stable for at least 5 days. Rats were then administered saline or increasing doses of the opioid antagonist naltrexone (NTX) (0.3, 1.0, 3.0, or 10.0 mg/kg) in order to determine antagonist-precipitated withdrawal. NTX precipitated withdrawal was similar in both morphine-maintained and M6S-maintained rats. In conclusion, the mixed μ/δ agonist activity of M6S failed to completely protect against the development of physical dependence, but delayed tolerance development to behavioral effects and resulted in decreased morphine-like subjective effects, perhaps implying a decreased abuse liability over μ agonists.
Keywords: abuse liability; delta opioid receptor (DOR); drug discrimination; mixed‐action mu/delta opioids; morphine; morphine‐6‐O‐sulfate (M6S); mu opioid receptor (MOR); physical dependence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antinociceptive effects of the 6-O-sulfate ester of morphine in normal and diabetic rats: Comparative role of mu- and delta-opioid receptors.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Nov;113(Pt A):335-347. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.09.012. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27637375 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Analgesia, Tolerance, and the Mechanism of Action of Morphine-6-O-Sulfate Across Multiple Pain Modalities in Sprague-Dawley Rats.Anesth Analg. 2017 Sep;125(3):1021-1031. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002006. Anesth Analg. 2017. PMID: 28489639 Free PMC article.
-
Discriminative stimulus effects of the mixed-opioid agonist/antagonist dezocine: cross-substitution by mu and delta opioid agonists.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Dec;283(3):1009-17. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997. PMID: 9399970
-
Biased Opioid Antagonists as Modulators of Opioid Dependence: Opportunities to Improve Pain Therapy and Opioid Use Management.Molecules. 2020 Sep 11;25(18):4163. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184163. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32932935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opioid regulation of mu receptor internalisation: relevance to the development of tolerance and dependence.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010 Nov;9(5):616-26. doi: 10.2174/187152710793361522. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20632966 Review.
Cited by
-
μ-opioid receptor agonists and psychedelics: pharmacological opportunities and challenges.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 11;14:1239159. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1239159. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37886127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mu-opioid mediated discriminative stimulus effects of fentanyl and xylazine: Dose-response and time-course studies.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2025 Jul 19;275:112799. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2025.112799. Online ahead of print. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2025. PMID: 40743692
References
-
- Neher E. Ion channels for communication between and within cells. Neuron. 1992;8:605‐612. - PubMed
-
- Preston KL, Jasinski DR. Abuse liability studies of opioid agonist‐antagonists in humans. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1991;28:49‐82. - PubMed
-
- Emmerson PJ, Clark MJ, Mansour A, Akil H, Woods JH, Medzihradsky F. Characterization of opioid agonist efficacy in a C6 glioma cell line expressing the mu opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;278:1121‐1127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

