Pediatric infratentorial subdural empyema: A case report
- PMID: 29930870
- PMCID: PMC5991265
- DOI: 10.4103/sni.sni_394_17
Pediatric infratentorial subdural empyema: A case report
Abstract
Background: Infratentorial subdural empyemas in children are extremely rare and potentially lethal intracranial infections. Delay in diagnosis and therapy is associated with increased morbidity and mortality.
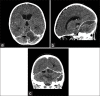
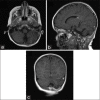
Case description: A 4-year-old boy presented with cerebellar signs following a failed treatment of otitis media. Imaging studies revealed a subdural empyema and left transverse and sigmoid sinus thrombosis. The empyema was evacuated operatively and antibiotic treatment was initiated and administered for 6 weeks. The patient recovered fully and was discharged 4 weeks following the evacuation of the empyema.
Conclusion: While prompt identification and treatment of subdural infratentorial empyemas are crucial for favorable outcomes, their diagnosis in children might be initially missed. This is, in part because they are so rare and in part, because imaging artifacts arising from the complex posterior fossa anatomy may obscure their presence in the computer tomography (CT) scan. Therefore, high level of suspicion is necessary, given the appropriate history and clinical presentation. In children, this is a recent history of protracted otitis media and central nervous system symptomatology-cerebellar or other.
Keywords: Child; empyema; infratentorial; pediatric; subdural.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Surgical Management of a Pediatric Infratentorial Subdural Empyema as a Complication of Parapharyngeal Abscess.Cureus. 2022 May 24;14(5):e25270. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25270. eCollection 2022 May. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35755555 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical challenge of recognizing infratentorial empyema.Neurology. 2007 Jul 31;69(5):477-81. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000266631.19745.32. Neurology. 2007. PMID: 17664407
-
Infratentorial subdural empyemas mimicking pyogenic meningitis.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013 Apr;4(2):213-5. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.112773. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013. PMID: 23914110 Free PMC article.
-
Which should be appropriate surgical treatment for subtentorial epidural empyema? Burr-hole evacuation versus decompressive craniectomy: Review of the literature with a case report.Asian J Neurosurg. 2016 Apr-Jun;11(2):81-6. doi: 10.4103/1793-5482.175630. Asian J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27057210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric intracranial subdural empyema caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis--a case report and review of literature.Childs Nerv Syst. 2010 Aug;26(8):1117-20. doi: 10.1007/s00381-010-1157-3. Epub 2010 May 2. Childs Nerv Syst. 2010. PMID: 20437243 Review.
Cited by
-
A Case of Subdural Empyema Due to Dental Pathogen.Cureus. 2023 Aug 17;15(8):e43666. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43666. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37724210 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical Management of a Pediatric Infratentorial Subdural Empyema as a Complication of Parapharyngeal Abscess.Cureus. 2022 May 24;14(5):e25270. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25270. eCollection 2022 May. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35755555 Free PMC article.
-
Subdural empyema in children.Childs Nerv Syst. 2018 Oct;34(10):1881-1887. doi: 10.1007/s00381-018-3907-6. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Childs Nerv Syst. 2018. PMID: 30014307 Review.
References
-
- Agrawal A, Timothy J, Pandit L, Shetty L, Shetty J. A review of subdural empyema and its management. Infect Dis Clin Pract. 2007;15:149–53.
-
- Borovich B, Johnston E, Spagnuolo E. Infratentorial subdural empyema: Clinical and computerized tomography findings. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg. 1990;72:299–301. - PubMed
-
- Calfee DP, Wispelwey B. Brain abscess, subdural empyema, and intracranial epidural abscess. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 1999;1:166–71. - PubMed
-
- Kanev PM, Salazar JC. Unusual CNS infection from a subtorcular dermal sinus. Acta Paediatr. 2010;99:627–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
