Management of autonomic dysreflexia associated with Charcot spinal arthropathy in a patient with complete spinal cord injury: Case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 29930879
- PMCID: PMC5991269
- DOI: 10.4103/sni.sni_287_17
Management of autonomic dysreflexia associated with Charcot spinal arthropathy in a patient with complete spinal cord injury: Case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Charcot spinal arthropathy (CSA) clearly represents a challenge in long-term spinal cord injury patients, one that can have extremely uncomfortable and potentially lethal outcomes if not managed properly.
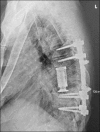
Case description: A 66-year-old man with a history of complete C7 quadriplegia presented with new-onset autonomic dysreflexia that resulted from Charcot spinal arthropathy (CSA). Pathologic instability, in the atypical site of the mid-thoracic spine, spanning from the T8-T9 vertebral levels was appreciated on physical exam as an audible, palpable, and visible dynamic kyphosis; kyphosis was later confirmed on neuroimaging. Based on the CSA severity and sequelae, the patient underwent bilateral decompression laminectomy with lateral extracavitary arthrodesis and posterior instrumentation. Symptoms dramatically improved and at 1-year follow-up, dynamic thoracic kyphosis and most symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia had resolved.
Conclusions: Based on our case and published reports, vigilant imaging and thorough physical examination in long-standing spinal cord injury could help early diagnosis and treatment of CSA, theoretically preventing development of cord atrophy and subsequent long-term sequelae. Surgical correction rather than bracing may be recommended in patients who have complete injury at or above T6 in patients with symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia associated with CSA confirmed on neuroimaging.
Keywords: Charcot spine; complications; long-term spinal cord injury; neuropathic spinal arthropathy; spinal neuroarthropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Arnold JM, Feng QP, Delaney GA, Teasell RW. Autonomic dysreflexia in tetraplegic patients: Evidence for alpha-adrenoceptor hyper-responsiveness. Clin Auton Res. 1995;5:267–70. - PubMed
-
- Baker N, Green A, Krishnan S, Rayman G. Microvascular and C-fiber function in diabetic charcot neuroarthropathy and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:3077–9. - PubMed
-
- Barrey C, Massourides H, Cotton F, Perrin G, Rode G. Charcot spine: Two new case reports and a systematic review of 109 clinical cases from the literature. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2010;53:200–20. - PubMed
-
- Beard JP, Wade WH, Barber DB. Sacral insufficiency stress fracture as etiology of positional autonomic dysreflexia: Case report. Paraplegia. 1996;34:173–5. - PubMed
-
- Bloch R. Autonomic dysfunction in management of spinal cord. In: Bloch RF, Basbaum M, editors. Management of Spinal Cord Injuries. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins; 1986. pp. 149–63.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
