Heparin Oligosaccharides Have Antiarrhythmic Effect by Accelerating the Sodium-Calcium Exchanger
- PMID: 29930947
- PMCID: PMC5999778
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00067
Heparin Oligosaccharides Have Antiarrhythmic Effect by Accelerating the Sodium-Calcium Exchanger
Abstract
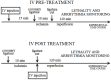
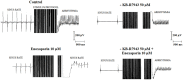
Background: Blockage of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) is used to determine the role of NCX in arrhythmogenesis. Trisulfated heparin disaccharide (TD) and Low Molecular Weight Heparins (LMWHs) can directly interact with the NCX and accelerate its activity. Objective: In this work, we investigated the antiarrhythmic effect of heparin oligosaccharides related to the NCX activity. Methods: The effects of heparin oligosaccharides were tested on the NCX current (patch clamping) and intracellular calcium transient in rat cardiomyocytes. The effects of heparin oligosaccharides were further investigated in arrhythmia induced in isolated rat atria and rats in vivo. Results: The intracellular Ca2+ concentration decreases upon treatment with either enoxaparin or ardeparin. These drugs abolished arrhythmia induction in isolated atria. The NCX antagonist KB-R7943 abolished the enoxaparin or ardeparin antiarrhythmic effects in isolated atria. In the in vivo measurements, injection of TD 15 min both before coronary occlusion or immediately after reperfusion, significantly prevented the occurrence of reperfusion-induced arrhythmias (ventricular arrhythmia and total AV block) and reduced the lethality rate. The patch clamping experiments showed that, mechanistically, TD increases the forward mode NCX current. Conclusion: Together, the data shows that heparin oligosaccharides may constitute a new class of antiarrhythmic drug that acts by accelerating the forward mode NCX under calcium overload.
Keywords: arrhythmia; calcium overload; low molecular weight heparin; sodium-calcium exchanger; trisulfated heparin disaccharide.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effect of heparin Trisulfated disaccharide on ischemic stroke.Glycoconj J. 2021 Feb;38(1):35-43. doi: 10.1007/s10719-020-09966-4. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Glycoconj J. 2021. PMID: 33411076
-
Effect of inhibition of Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger at the time of myocardial reperfusion on hypercontracture and cell death.Cardiovasc Res. 2002 Sep;55(4):739-48. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(02)00461-3. Cardiovasc Res. 2002. PMID: 12176123
-
The Effect of a Novel Highly Selective Inhibitor of the Sodium/Calcium Exchanger (NCX) on Cardiac Arrhythmias in In Vitro and In Vivo Experiments.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 10;11(11):e0166041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166041. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27832106 Free PMC article.
-
Topics on the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger: pharmacological characterization of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger inhibitors.J Pharmacol Sci. 2006 Sep;102(1):7-16. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fmj06002x2. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16990699 Review.
-
Na+/Ca2+ exchange inhibitors: a new class of calcium regulators.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2007 Sep;7(3):188-98. doi: 10.2174/187152907781745288. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17896959 Review.
Cited by
-
Straight to the heart: Pleiotropic antiarrhythmic actions of oral anticoagulants.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Jul;145:104257. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104257. Epub 2019 May 2. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 31054953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticoagulant and antiarrhythmic effects of heparin in the treatment of COVID-19 patients.J Thromb Haemost. 2020 Aug;18(8):2073-2075. doi: 10.1111/jth.14902. J Thromb Haemost. 2020. PMID: 32408391 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pharmacological Modulation by Low Molecular Weight Heparin of Purinergic Signaling in Cardiac Cells Prevents Arrhythmia and Lethality Induced by Myocardial Infarction.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Feb 27;10(3):103. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10030103. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 36975867 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of heparin Trisulfated disaccharide on ischemic stroke.Glycoconj J. 2021 Feb;38(1):35-43. doi: 10.1007/s10719-020-09966-4. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Glycoconj J. 2021. PMID: 33411076
-
Targeting Ca2 + Handling Proteins for the Treatment of Heart Failure and Arrhythmias.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 4;11:1068. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.01068. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33013458 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Szepesi J, Acsai K, Sebok Z, Prorok J, Pollesello P, Levijoki J, et al. . Comparison of the efficiency of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger or Na+/H+ exchanger inhibition and their combination in reducing coronary reperfusion-induced arrhythmias. J Physiol Pharmacol. (2015) 66:215–26. - PubMed
-
- Amran MS, Homma N, Hashimoto K. Effects of sea0400 on ouabain-induced arrhythmias in guinea pigs. J Sci Res. (2012) 4:213–25. 10.3329/jsr.v4i1.7722 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

