Organic Solute Transporter α-β Protects Ileal Enterocytes From Bile Acid-Induced Injury
- PMID: 29930976
- PMCID: PMC6009794
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.01.006
Organic Solute Transporter α-β Protects Ileal Enterocytes From Bile Acid-Induced Injury
Abstract
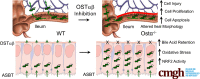
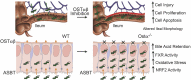
Background & aims: Ileal bile acid absorption is mediated by uptake via the apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT), and export via the basolateral heteromeric organic solute transporter α-β (OSTα-OSTβ). In this study, we investigated the cytotoxic effects of enterocyte bile acid stasis in Ostα-/- mice, including the temporal relationship between intestinal injury and initiation of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids.
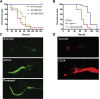
Methods: Ileal tissue morphometry, histology, markers of cell proliferation, gene, and protein expression were analyzed in male and female wild-type and Ostα-/- mice at postnatal days 5, 10, 15, 20, and 30. Ostα-/-Asbt-/- mice were generated and analyzed. Bile acid activation of intestinal Nrf2-activated pathways was investigated in Drosophila.
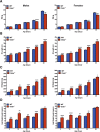
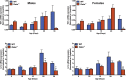
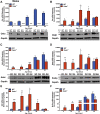
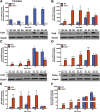
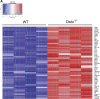
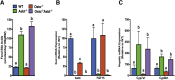
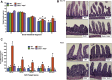
Results: As early as day 5, Ostα-/- mice showed significantly increased ileal weight per length, decreased villus height, and increased epithelial cell proliferation. This correlated with premature expression of the Asbt and induction of bile acid-activated farnesoid X receptor target genes in neonatal Ostα-/- mice. Expression of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-1 and Nrf2-anti-oxidant responsive genes were increased significantly in neonatal Ostα-/- mice at these postnatal time points. Bile acids also activated Nrf2 in Drosophila enterocytes and enterocyte-specific knockdown of Nrf2 increased sensitivity of flies to bile acid-induced toxicity. Inactivation of the Asbt prevented the changes in ileal morphology and induction of anti-oxidant response genes in Ostα-/- mice.
Conclusions: Early in postnatal development, loss of Ostα leads to bile acid accumulation, oxidative stress, and a restitution response in ileum. In addition to its essential role in maintaining bile acid homeostasis, Ostα-Ostβ functions to protect the ileal epithelium against bile acid-induced injury. NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus: GSE99579.
Keywords: ARE, anti-oxidant response element; Asbt, apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; Drosophila; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GFP, green fluorescence protein; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; Ibabp, ileal bile acid binding protein; Ileum; NEC, necrotizing enterocolitis; Neonate; Nox, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase; Nrf2, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2; Nuclear Factor Erythroid-Derived 2-Like 2; Ost, organic solute transporter; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Reactive Oxygen Species; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase–mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling; WT, wild type; cRNA, complementary RNA; mRNA, messenger RNA.
Figures



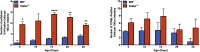


References
-
- Ballatori N., Christian W.V., Lee J.Y., Dawson P.A., Soroka C.J., Boyer J.L., Madejczyk M.S., Li N. OSTalpha-OSTbeta: a major basolateral bile acid and steroid transporter in human intestinal, renal, and biliary epithelia. Hepatology. 2005;42:1270–1279. - PubMed
-
- Heubi J.E., Balistreri W.F., Fondacaro J.D., Partin J.C., Schubert W.K. Primary bile acid malabsorption: defective in vitro ileal active bile acid transport. Gastroenterology. 1982;83:804–811. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

