HS6ST1 Insufficiency Causes Self-Limited Delayed Puberty in Contrast With Other GnRH Deficiency Genes
- PMID: 29931354
- PMCID: PMC6126894
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2018-00646
HS6ST1 Insufficiency Causes Self-Limited Delayed Puberty in Contrast With Other GnRH Deficiency Genes
Abstract
Context: Self-limited delayed puberty (DP) segregates in an autosomal-dominant pattern, but the genetic basis is largely unknown. Although DP is sometimes seen in relatives of patients with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH), mutations in genes known to cause HH that segregate with the trait of familial self-limited DP have not yet been identified.
Objective: To assess the contribution of mutations in genes known to cause HH to the phenotype of self-limited DP.
Design, patients, and setting: We performed whole-exome sequencing in 67 probands and 93 relatives from a large cohort of familial self-limited DP, validated the pathogenicity of the identified gene variant in vitro, and examined the tissue expression and functional requirement of the mouse homolog in vivo.
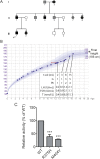
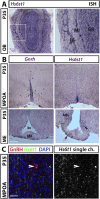
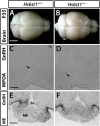
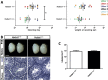
Results: A potentially pathogenic gene variant segregating with DP was identified in 1 of 28 known HH genes examined. This pathogenic variant occurred in HS6ST1 in one pedigree and segregated with the trait in the six affected members with heterozygous transmission (P = 3.01 × 10-5). Biochemical analysis showed that this mutation reduced sulfotransferase activity in vitro. Hs6st1 mRNA was expressed in peripubertal wild-type mouse hypothalamus. GnRH neuron counts were similar in Hs6st1+/- and Hs6st1+/+ mice, but vaginal opening was delayed in Hs6st1+/- mice despite normal postnatal growth.
Conclusions: We have linked a deleterious mutation in HS6ST1 to familial self-limited DP and show that heterozygous Hs6st1 loss causes DP in mice. In this study, the observed overlap in potentially pathogenic mutations contributing to the phenotypes of self-limited DP and HH was limited to this one gene.
Figures

References
-
- Ritte R, Lukanova A, Tjonneland A, Olsen A, Overvad K, Mesrine S, Fagherazzi G, Dossus L, Teucher B, Steindorf K, Boeing H, Aleksandrova K, Trichopoulou A, Lagiou P, Trichopoulos D, Palli D, Grioni S, Mattiello A, Tumino R, Sacerdote C, Quiros JR, Buckland G, Molina-Montes E, Chirlaque MD, Ardanaz E, Amiano P, Bueno-de-Mesquita B, van Duijnhoven F, van Gils CH, Peeters PH, Wareham N, Khaw KT, Key TJ, Travis RC, Krum-Hansen S, Gram IT, Lund E, Sund M, Andersson A, Romieu I, Rinaldi S, McCormack V, Riboli E, Kaaks R. Height, age at menarche and risk of hormone receptor-positive and -negative breast cancer: a cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(11):2619–2629. - PubMed
-
- Sedlmeyer IL, Hirschhorn JN, Palmert MR. Pedigree analysis of constitutional delay of growth and maturation: determination of familial aggregation and inheritance patterns. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(12):5581–5586. - PubMed
-
- Wehkalampi K, Widén E, Laine T, Palotie A, Dunkel L. Patterns of inheritance of constitutional delay of growth and puberty in families of adolescent girls and boys referred to specialist pediatric care. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(3):723–728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/K020455/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 102745/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/L002671/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/L002639/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

