Aporrectodea caliginosa, a relevant earthworm species for a posteriori pesticide risk assessment: current knowledge and recommendations for culture and experimental design
- PMID: 29931645
- PMCID: PMC6245014
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-018-2579-9
Aporrectodea caliginosa, a relevant earthworm species for a posteriori pesticide risk assessment: current knowledge and recommendations for culture and experimental design
Abstract
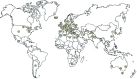
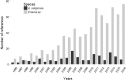
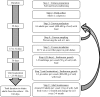
Ecotoxicological tests with earthworms are widely used and are mandatory for the risk assessment of pesticides prior to registration and commercial use. The current model species for standardized tests is Eisenia fetida or Eisenia andrei. However, these species are absent from agricultural soils and often less sensitive to pesticides than other earthworm species found in mineral soils. To move towards a better assessment of pesticide effects on non-target organisms, there is a need to perform a posteriori tests using relevant species. The endogeic species Aporrectodea caliginosa (Savigny, 1826) is representative of cultivated fields in temperate regions and is suggested as a relevant model test species. After providing information on its taxonomy, biology, and ecology, we reviewed current knowledge concerning its sensitivity towards pesticides. Moreover, we highlighted research gaps and promising perspectives. Finally, advice and recommendations are given for the establishment of laboratory cultures and experiments using this soil-dwelling earthworm species.
Keywords: Agroecosystems; Agroecotoxicology; Aporrectodea caliginosa; Breeding; Lumbricidae; Plant protection products; Soil ecotoxicology.
Figures


References
-
- Alshawish SA, Mohamed AI, Nair GA. Prolonged toxicity of sub-lethal dosages of chemical pesticides on the body mass and cocoons of Aporrectodea caliginosa (Savigny 1826) (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae) inhabiting Benghazi, Libya. Proc Natl Acad Sci India B Biol Sci. 2004;74:123–133.
-
- Badawy MEI, Kenawy A, El-Aswad AF (2013) Toxicity assessment of buprofezin, lufenuron, and triflumuron to the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa. Int J Zool 174523-Article ID 174523
-
- Bertrand M, Barot S, Blouin M, Whalen J, de Oliveira T, Roger-Estrade J. Earthworm services for cropping systems. A review. Agron Sustain Dev. 2015;35:553–567. doi: 10.1007/s13593-014-0269-7. - DOI
-
- Blouin M, Hodson ME, Delgado EA, Baker G, Brussaard L, Butt KR, Dai J, Dendooven L, Peres G, Tondoh JE, Cluzeau D, Brun JJ. A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. Eur J Soil Sci. 2013;64:161–182. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12025. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

