Estimating the prevalence of chronic hepatitis C virus infection in New York City, 2015
- PMID: 29932040
- PMCID: PMC9507940
- DOI: 10.1017/S095026881800170X
Estimating the prevalence of chronic hepatitis C virus infection in New York City, 2015
Abstract
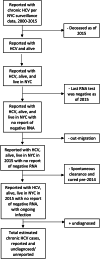
Chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most common blood-borne infection in the USA. Estimating prevalence is critical for monitoring diagnosis, treatment, and cure and for allocating resources. Surveillance data reported to the New York City (NYC) Health Department, 2000-2015, were used to estimate HCV prevalence in NYC in 2015. The numbers who died, out-migrated or whose last RNA test was negative were removed from the count of people reported with HCV. A simulation model was used to remove estimates of people whose infection spontaneously cleared or was cured and to add an estimate of people unaware of infection. The surveillance-based HCV prevalence in NYC in 2015 overall was 1.4% (95% certainty level (CL) 1.2-1.6%; n ≈ 116 000, 95% CL ≈99 000-135 000) and among adults aged ⩾20 years was 1.8% (95% CL 1.5-2.0%, n ≈ 115 000, 95% CL ≈99 000-134 000), lower than the 2010 estimate among adults aged ⩾20 years of 2.4% (n ≈ 147 000). Contributors to the decrease in HCV prevalence from 2010 to 2015 include both the availability of highly effective treatment and also deaths among an ageing population. The 2015 estimate can be used to set NYC-specific HCV screening and treatment targets and monitor progress towards HCV elimination.
Keywords: Estimating; hepatitis C; prevalence of disease; surveillance.
Figures
References
-
- Alter MJ et al. (1999) The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1988 through 1994. New England Journal of Medicine 341, 556–562. - PubMed
-
- Davis GL et al. (2003) Projecting future complications of chronic hepatitis C in the United States. Liver Transplantation 9, 331–338. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources