Protective Effects of Xyloglucan in Association with the Polysaccharide Gelose in an Experimental Model of Gastroenteritis and Urinary Tract Infections
- PMID: 29932149
- PMCID: PMC6073600
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19071844
Protective Effects of Xyloglucan in Association with the Polysaccharide Gelose in an Experimental Model of Gastroenteritis and Urinary Tract Infections
Abstract
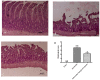
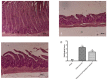
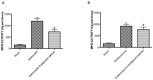
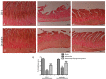
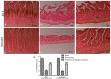
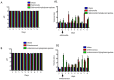
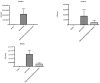
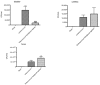
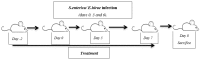
Acute infectious gastroenteritis (GE) and urinary tract infection (UTI) are common diseases and are normally perceived as mild and limiting illnesses. Xyloglucan is a natural plant polymer with protective barrier properties, also known as “mucosal protectors”, which is the main ingredient of medical devices developed for the management of different diseases, such as gastrointestinal diseases, urinary tract infections, or respiratory allergic diseases. The aim of this study was to evaluate the protective effect of xyloglucan in association with gelose (also called agar) in an experimental model of bacterial GE and UTI in rats. Two kinds of infection were induced by oral administration of Salmonella enterica and Enterococcus hirae for three days. Two days before the bacterial administration, preventive oral treatment with xyloglucan + gelose (10 mg/kg + 5 mg/kg) was performed daily until the seventh day. Twenty-four hours after the last treatment, rats were sacrificed and urinary tracts and intestines for different analysis were collected. The results showed that xyloglucan plus gelose was able to reduce intestinal morphological changes (p < 0.05 for both), tight junctions (TJ) permeability (p < 0.001 for both), and neutrophil infiltration (p < 0.05 for both) induced by bacterial infections, highlighting its barrier proprieties. Moreover, the compound reduced the number of bacterial colonies in the urinary tract favoring elimination by feces. The results obtained in the present study suggest that the protective barrier properties of xyloglucan plus gelose allow the prevention of GE and UTI in models of infections in rats.
Keywords: gastroenteritis; gelose; urinary tract infection; xyloglucan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Xyloglucan against Escherichia coli Extraintestinal Urinary Tract Infection: An in vivo Study.Microb Physiol. 2020;30(1-6):50-60. doi: 10.1159/000510874. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Microb Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33070135
-
Xyloglucan, a Plant Polymer with Barrier Protective Properties over the Mucous Membranes: An Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 27;19(3):673. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030673. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29495535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xyloglucan + Gelose Combination versus Placebo as Adjuvant Therapy to First-Line Antimicrobials for Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection in Adults.Urol Int. 2019;102(4):468-475. doi: 10.1159/000497106. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Urol Int. 2019. PMID: 30889607 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of xyloglucan and gelose for the treatment of acute diarrhea in children.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Mar;15(3):325-331. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1833715. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33028102 Clinical Trial.
-
A case of urinary tract infection due to Salmonella enterica serovar Virchow and review of the related literature.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2012 Mar;59(1):85-9. doi: 10.1556/AMicr.59.2012.1.9. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2012. PMID: 22510290 Review.
Cited by
-
Properties of a New Food Supplement Containing Actinia equina Extract.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Oct 1;9(10):945. doi: 10.3390/antiox9100945. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33019631 Free PMC article.
-
Present and Future Therapeutic Approaches to Barrier Dysfunction.Front Nutr. 2021 Oct 28;8:718093. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.718093. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34778332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of xyloglucan associations with gelatin or gelose on Escherichia coli-derived lipopolysaccharide-induced enteritis in rats.Drugs Context. 2023 Oct 26;12:2023-5-2. doi: 10.7573/dic.2023-5-2. eCollection 2023. Drugs Context. 2023. PMID: 37908642 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a Product Containing Xyloglucan and Pea Protein on a Murine Model of Atopic Dermatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 19;21(10):3596. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103596. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32438777 Free PMC article.
-
Topical Delivery of Curcumin by Choline-Calix[4]arene-Based Nanohydrogel Improves Its Therapeutic Effect on a Psoriasis Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 17;21(14):5053. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145053. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32708987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skyum F., Andersen V., Chen M., Pedersen C., Mogensen C.B. Infectious Gastroenteritis and the Need for Strict Contact Precaution Procedures in Adults Presenting in the Emergency Department—A Danish Register-based Study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018;98:391–397. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2017.11.001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

