siRNAs Targeting Growth Factor Receptor and Anti-Apoptotic Genes Synergistically Kill Breast Cancer Cells through Inhibition of MAPK and PI-3 Kinase Pathways
- PMID: 29932151
- PMCID: PMC6164725
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines6030073
siRNAs Targeting Growth Factor Receptor and Anti-Apoptotic Genes Synergistically Kill Breast Cancer Cells through Inhibition of MAPK and PI-3 Kinase Pathways
Abstract
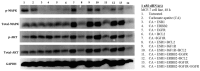
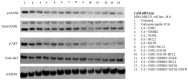
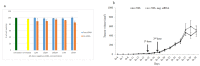
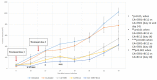
Breast cancer, the second leading cause of female deaths worldwide, is usually treated with cytotoxic drugs, accompanied by adverse side-effects, development of chemoresistance and relapse of disease condition. Survival and proliferation of the cancer cells are greatly empowered by over-expression or over-activation of growth factor receptors and anti-apoptotic factors. Identification of these key players that cross-talk to each other, and subsequently, knockdown with their respective siRNAs in a synchronous manner could be a promising approach to precisely treat the cancer. Since siRNAs demonstrate limited cell permeability and unfavorable pharmacokinetic behaviors, pH-sensitive nanoparticles of carbonate apatite were employed to efficiently carry the siRNAs in vitro and in vivo. By delivering selective siRNAs against the mRNA transcripts of the growth factor receptors, such as ER, ERBB2 (HER2), EGFR and IGFR, and anti-apoptotic protein, such as BCL2 in human (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) and murine (4T1) breast cancer cell lines, we found that ESR1 along with BCL-2, or with ERBB2 and EGFR critically contributes to the growth/survival of the cancer cells by activating the MAPK and PI-3 kinase pathways. Furthermore, intravenous delivery of the selected siRNAs aiming to suppress the expression of ER/BCL2 and ER/ERBB2/EGFR groups of proteins led to a significant retardation in tumor growth in a 4T1-induced syngeneic mouse model.
Keywords: breast cancer; carbonate apatite nanoparticle; estrogen receptor (ER); mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); protein kinase B (AKT); siRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- De Moraes G.N., Delbue D., Silva K.L., Robaina M.C., Khongkow P., Gomes A.R., Zona S., Crocamo S., Mencalha A.L., Magalhães L.M., et al. FOXM1 targets XIAP and survivin to modulate breast cancer survival and chemoresistance. Cell Signal. 2015;27:2496–2505. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.09.013. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

