Emergence of Integrase Resistance Mutations During Initial Therapy Containing Dolutegravir
- PMID: 29933437
- PMCID: PMC6093998
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciy228
Emergence of Integrase Resistance Mutations During Initial Therapy Containing Dolutegravir
Abstract
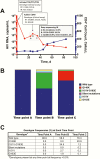
Dolutegravir (DTG) is a preferred drug for initial treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. We present next-generation sequencing analysis of integrase genotypes during a period of virologic failure in a treatment-naive man who initiated tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine plus DTG.
Figures
References
-
- Cahn P, Pozniak AL, Mingrone H, et al. ; extended SAILING Study Team Dolutegravir versus raltegravir in antiretroviral-experienced, integrase-inhibitor-naive adults with HIV: week 48 results from the randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority SAILING study. Lancet 2013; 382:700–8. - PubMed
-
- Walmsley SL, Antela A, Clumeck N, et al. ; SINGLE Investigators Dolutegravir plus abacavir-lamivudine for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med 2013; 369:1807–18. - PubMed
-
- Clotet B, Feinberg J, van Lunzen J, et al. ; ING114915 Study Team Once-daily dolutegravir versus darunavir plus ritonavir in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 infection (FLAMINGO): 48 week results from the randomised open-label phase 3b study. Lancet 2014; 383:2222–31. - PubMed
-
- Raffi F, Jaeger H, Quiros-Roldan E, et al. ; extended SPRING-2 Study Group Once-daily dolutegravir versus twice-daily raltegravir in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 infection (SPRING-2 study): 96 week results from a randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2013; 13:927–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

