Pain Modulation after Oromucosal Cannabinoid Spray (SATIVEX®) in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Study with Quantitative Sensory Testing and Laser-Evoked Potentials
- PMID: 29933552
- PMCID: PMC6163235
- DOI: 10.3390/medicines5030059
Pain Modulation after Oromucosal Cannabinoid Spray (SATIVEX®) in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Study with Quantitative Sensory Testing and Laser-Evoked Potentials
Abstract
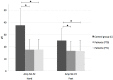
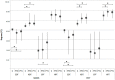
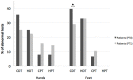
Background. Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)/cannabidiol (CBD) (nabiximols or Sativex®) is an oromucosal spray formulation containing THC and CBD at an approximately 1:1 fixed ratio. Its administration for the treatment of pain in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) has been established. MS patients generally complain of different kinds of pain, including spasticity-related and neuropathic pain. In this study, we compared and evaluated pain modulation and thermal/pain threshold of MS patients before and after THC/CBD administration. Methods. 19 MS patients underwent clinical examination, numerical rating scale (NRS), quantitative sensory testing (QST), and laser-evoked potentials (LEPs) before and after 1 month of therapy. Psychophysiological and neurophysiological data were compared to sex- and age-matched controls. Results. Patients reported a significant reduction in pain. We found statistically significant differences in LEP parameters between patients and controls but no significant change in LEP measures after THC/CBD therapy. Cold and heat detection thresholds were altered in patients but did not change after THC/CBD therapy. There was a significant increase in cold pain threshold by hand stimulation and a significant reduction in abnormal cold perception thresholds. Conclusions. Our results indicate that Sativex® therapy provides pain relief in MS patients and suggest that it might modulate peripheral cold-sensitive TRP channels.
Keywords: laser-evoked potentials; multiple sclerosis; oromucosal cannabinoid spray; pain; quantitative sensory testing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Indaco A., Iachetta C., Nappi C., Socci L., Carrieri P.B. Chronic and acute pain syndromes in patients with multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. 1994;16:97–102. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

