Calcium-Binding Proteins S100A8 and S100A9: Investigation of Their Immune Regulatory Effect in Myeloid Cells
- PMID: 29933628
- PMCID: PMC6073713
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19071833
Calcium-Binding Proteins S100A8 and S100A9: Investigation of Their Immune Regulatory Effect in Myeloid Cells
Abstract
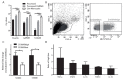
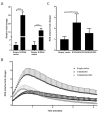
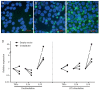
High expression levels of the calcium-binding proteins S100A8 and S100A9 in myeloid cells in kidney transplant rejections are associated with a favorable outcome. Here we investigated the myeloid cell subset expressing these molecules, and their function in inflammatory reactions. Different monocyte subsets were sorted from buffy coats of healthy donors and investigated for S100A8 and S100A9 expression. To characterize S100A9high and S100A9low subsets within the CD14+ classical monocyte subset, intracellular S100A9 staining was combined with flow cytometry (FACS) and qPCR profiling. Furthermore, S100A8 and S100A9 were overexpressed by transfection in primary monocyte-derived macrophages and the THP-1 macrophage cell line to investigate the functional relevance. Expression of S100A8 and S100A9 was primarily found in classical monocytes and to a much lower extent in intermediate and non-classical monocytes. All S100A9+ cells expressed human leukocyte antigen—antigen D related (HLA-DR) on their surface. A small population (<3%) of CD14+ CD11b+ CD33+ HLA-DR− cells, characterized as myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), also expressed S100A9 to high extent. Overexpression of S100A8 and S00A9 in macrophages led to enhanced extracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, as well as elevated mRNA expression of anti-inflammatory IL-10. The results suggest that the calcium-binding proteins S100A8 and S100A9 in myeloid cells have an immune regulatory effect.
Keywords: S100A9 subsets; calcium-binding proteins; immune regulation; monocytes subsets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Frosch M., Strey A., Vogl T., Wulffraat N.M., Kuis W., Sunderkötter C., Harms E., Sorg C., Roth J. Myeloid-related proteins 8 and 14 are specifically secreted during interaction of phagocytes and activated endothelium and are useful markers for monitoring disease activity in pauciarticular-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2000;43:628–637. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200003)43:3<628::AID-ANR20>3.0.CO;2-X. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

