Cutaneous and Mucosal Manifestations Associated with Celiac Disease
- PMID: 29933630
- PMCID: PMC6073559
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10070800
Cutaneous and Mucosal Manifestations Associated with Celiac Disease
Abstract
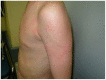
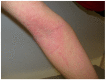
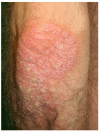
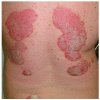
Celiac disease (CD) is an immune-mediated, gluten-induced enteropathy that affects predisposed individuals of all ages. Many patients with CD do not report gastrointestinal symptoms making it difficult to reach an early diagnosis. On the other hand, CD is related to a wide spectrum of extra-intestinal manifestations, with dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) being the best characterized. These associated conditions may be the clue to reaching the diagnosis of CD. Over the last few years, there have been multiple reports of the association between CD and several cutaneous manifestations that may improve with a gluten-free diet (GFD). The presence of some of these skin diseases, even in the absence of gastrointestinal symptoms, should give rise to an appropriate screening method for CD. The aim of this paper is to describe the different cutaneous manifestations that have been associated with CD and the possible mechanisms involved.
Keywords: alopecia areata; atopic dermatitis; celiac disease; cutaneous vasculitis; dermatitis herpetiformis; gluten-free diet; psoriasis; recurrent aphtous ulceration; rosacea; urticaria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

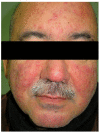

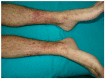
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

