Developments with investigating descriptors for antimicrobial AApeptides and their derivatives
- PMID: 29933702
- PMCID: PMC6301047
- DOI: 10.1080/17460441.2018.1487950
Developments with investigating descriptors for antimicrobial AApeptides and their derivatives
Abstract
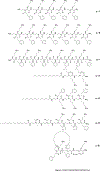
The development of multidrug-resistant strains of bacteria resulting from prolonged treatment with conventional antibiotics has necessitated the need for continuous research for better antibiotic strategies. One of these alternatives is evolutionary antimicrobial peptides also known as host-defense peptides (HDPs). HDPs are an integral part of the innate defense system in multicellular eukaryotes. Although HDPs can largely circumvent the persistent problem of antibiotic resistance due to their bacteriolytic membrane mechanism, they have some drawbacks including a low activity profile and protease instability. AApeptides have recently been introduced as a new class of peptidomimetics with resistance to proteolysis, improved activity profile, and limitless possibilities for structural diversity. Furthermore, they have shown excellent antimicrobial activity. Areas covered: This review updates the reader on the latest developments of antimicrobial AApeptides, the various derivatizations, and their development for antimicrobial applications. The most recent findings on the heterogeneous γ-AA backbone are also outlined. Expert opinion: AApeptides have found diverse applications in antimicrobial studies. AApeptides are believed to exhibit bactericidal properties by imitating the membranolytic action of HDPs. They have shown broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and are active against medicinally relevant drug-resistant pathogens. AApeptides and their derivatives could gain therapeutic relevance in the design and development of antibiotic agents.
Keywords: AApeptides; antibiotic resistance; antimicrobial activity; antimicrobial peptides; antimicrobial peptidomimetics; host-defense peptides (HDPs).
Figures
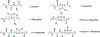



References
-
- Projan SJ. Why is big Pharma getting out of antibacterial drug discovery? Curr Opin Microbiol 2003;6(5):427–30. - PubMed
-
- Endres BT, Bassères E, Alam MJ, et al. Cadazolid for the treatment of Clostridium difficile. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2017;26(4):509–14. - PubMed
-
- Tomasz A Multiple-Antibiotic-Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria -- A Report on the Rockefeller University Workshop. N Engl J Med 1994;330(17):1247–51. - PubMed
-
- Murray BE. Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcal Infections. N Engl J Med 2000;342(10):710–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
