Infective Endocarditis After Melody Valve Implantation in the Pulmonary Position: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 29934419
- PMCID: PMC6064882
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.008163
Infective Endocarditis After Melody Valve Implantation in the Pulmonary Position: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Infective endocarditis (IE) after transcatheter pulmonary valve implantation (TPVI) in dysfunctioning right ventricular outflow tract conduits has evoked growing concerns. We aimed to investigate the incidence and the natural history of IE after TPVI with the Melody valve through a systematic review of published data.
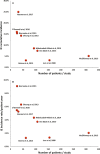
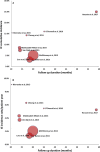
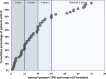
Methods and results: PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science databases were systematically searched for articles published until March 2017, reporting on IE after TPVI with the Melody valve. Nine studies (including 851 patients and 2060 patient-years of follow-up) were included in the analysis of the incidence of IE. The cumulative incidence of IE ranged from 3.2% to 25.0%, whereas the annualized incidence rate ranged from 1.3% to 9.1% per patient-year. The median (interquartile range) time from TPVI to the onset of IE was 18.0 (9.0-30.4) months (range, 1.0-72.0 months). The most common findings were positive blood culture (93%), fever (89%), and new, significant, and/or progressive right ventricular outflow tract obstruction (79%); vegetations were detectable on echocardiography in only 34% of cases. Of 69 patients with IE after TPVI, 6 (8.7%) died and 35 (52%) underwent surgical and/or transcatheter reintervention. Death or reintervention was more common in patients with new/significant right ventricular outflow tract obstruction (69% versus 33%; P=0.042) and in patients with non-streptococcal IE (73% versus 30%; P=0.001).
Conclusions: The incidence of IE after implantation of a Melody valve is significant, at least over the first 3 years after TPVI, and varies considerably between the studies. Although surgical/percutaneous reintervention is a common consequence, some patients can be managed medically, especially those with streptococcal infection and no right ventricular outflow tract obstruction.
Keywords: Melody valve; congenital heart disease; endocarditis; percutaneous pulmonary valve implantation; percutaneous valve; pulmonary valve; transcatheter valve implantation.
© 2018 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures

References
-
- Bonhoeffer P, Boudjemline Y, Saliba Z, Merckx J, Aggoun Y, Bonnet D, Acar P, Le Bidois J, Sidi D, Kachaner J. Percutaneous replacement of pulmonary valve in a right‐ventricle to pulmonary‐artery prosthetic conduit with valve dysfunction. Lancet. 2000;356:1403–1405. - PubMed
-
- Zahn EM, Hellenbrand WE, Lock JE, McElhinney DB. Implantation of the melody transcatheter pulmonary valve in patients with a dysfunctional right ventricular outflow tract conduit early results from the U.S. clinical trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:1722–1729. - PubMed
-
- Cheatham JP, Hellenbrand WE, Zahn EM, Jones TK, Berman DP, Vincent JA, McElhinney DB. Clinical and hemodynamic outcomes up to 7 years after transcatheter pulmonary valve replacement in the US melody valve investigational device exemption trial. Circulation. 2015;131:1960–1970. - PubMed
-
- Uebing A, Rigby ML. The problem of infective endocarditis after transcatheter pulmonary valve implantation. Heart. 2015;101:749–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

