Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism in Men With Diabesity
- PMID: 29934480
- PMCID: PMC6014549
- DOI: 10.2337/dc17-2510
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism in Men With Diabesity
Abstract
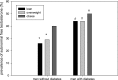
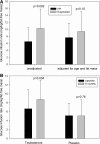
One-third of men with obesity or type 2 diabetes have subnormal free testosterone concentrations. The lower free testosterone concentrations are observed in obese men at all ages, including adolescents at completion of puberty. The gonadotropin concentrations in these males are inappropriately normal; thus, these patients have hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH). The causative mechanism of diabesity-induced HH is yet to be defined but is likely multifactorial. Decreased insulin and leptin signaling in the central nervous system are probably significant contributors. Contrary to popular belief, estrogen concentrations are lower in men with HH. Men with diabesity and HH have more fat mass and are more insulin resistant than eugonadal men. In addition, they have a high prevalence of anemia and higher mortality rates than eugonadal men. Testosterone replacement therapy results in a loss of fat mass, gain in lean mass, and increase in insulin sensitivity in men with diabesity and HH. This is accompanied by an increase in insulin-signaling genes in adipose tissue and a reduction in inflammatory mediators that interfere with insulin signaling. There is also an improvement in sexual symptoms, anemia, LDL cholesterol, and lipoprotein (a). However, testosterone therapy does not consistently affect HbA1c in men with diabetes. The effect of testosterone replacement on cardiovascular events or mortality in men with diabesity is not known and remains to be studied in prospective trials.
© 2018 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures


References
-
- Dhindsa S, Prabhakar S, Sethi M, Bandyopadhyay A, Chaudhuri A, Dandona P. Frequent occurrence of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89:5462–5468 - PubMed
-
- Bhasin S, Brito JP, Cunningham GR, et al. Testosterone therapy in men with hypogonadism: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2018;103:1715–1744 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

