The effect of intrathecal dexmedetomidine on the dose requirement of hyperbaric bupivacaine in spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized study
- PMID: 29935528
- PMCID: PMC6015661
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-018-0528-2
The effect of intrathecal dexmedetomidine on the dose requirement of hyperbaric bupivacaine in spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section: a prospective, double-blinded, randomized study
Abstract
Background: Studies have shown that dexmedetomidine (Dex) can prolong the duration of analgesia when added to local anaesthetic as an adjuvant in a central or peripheral nerve block. We hypothesized that intrathecal Dex can reduce the ED95 of spinal hyperbaric bupivacaine. Therefore, we conducted this prospective, double-blinded, randomized study to verify our hypothesis.
Methods: Ninety patients were allocated into the Dexmedetomidine group (received bupivacaine + 5 mcg dexmedetomidine) and the Control group (received bupivacaine + the same volume of saline) using a double-blinded and randomized method. The first patient in each group received 5 mg of IT hyperbaric bupivacaine, and the next dose for the following patient was determined by the probability of successful anaesthesia of the previous neighbouring dose. An improved up-down sequence allocated method combined with probit analysis was used to determine the ED95 of intrathecal hyperbaric bupivacaine for the two groups.
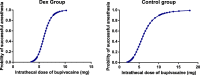
Results: The ED95 and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) of IT hyperbaric bupivacaine of the Dex group and Control group were 8.4 mg (95% CI, 6.5~ 13.8 mg) and 12.1 mg (95% CI, 8.3~ 312.8 mg), respectively. The duration of sensory block was longer in the Dex group than in the Control group (110.3 ± 35.3 vs 67.5 ± 26.2). The duration of analgesia was also longer in the Dex group than in the Control group (224.9 ± 45.4 vs 155.1 ± 31.6). The consumption of postoperative rescued sufentanil was significantly higher in the Control group than in the Dex group.
Conclusion: Intrathecal 5 mcg dexmedetomidine potentiated hyperbaric bupivacaine antinociception by 31% in spinal anaesthesia for patients undergoing caesarean section.
Trial registration: We registered this study in a Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR) centre on Nov 1st 2016 and received the registration number: ChiCTR-IPR-16009699 .
Keywords: Bupivacaine; Caesarean section; Dexmedetomidine; Dose-response; Intrathecal.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Jiaxing University Affiliated Women and Children Hospital (Batch No.: 201600328; 10th, Oct, 2016), and written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Gizzo S, Noventa M, Fagherazzi S, Lamparelli L, Ancona E, Di Gangi S, Saccardi C, D'Antona D, Nardelli GB. Update on best available options in obstetrics anaesthesia: perinatal outcomes, side effects and maternal satisfaction. Fifteen years systematic literature review. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;290:21–34. doi: 10.1007/s00404-014-3454-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical