Fish oil-derived lipid emulsion induces RIP1-dependent and caspase 8-licensed necroptosis in IEC-6 cells through overproduction of reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 29935529
- PMCID: PMC6015656
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-018-0786-5
Fish oil-derived lipid emulsion induces RIP1-dependent and caspase 8-licensed necroptosis in IEC-6 cells through overproduction of reactive oxygen species
Abstract
Background: Excessive cell death of enterocytes has been demonstrated to be partially associated with the intravenously-administrated lipid emulsions (LEs) during parenteral nutrition (PN) support. However, as a new generation of LE, the effect of fish oil-derived lipid emulsion (FOLE) on the death of enterocytes remains elusive.
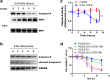
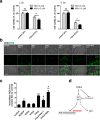
Methods: Intestinal epithelial cells (IEC-6 cell line) were treated with FOLE (0.25-1%) for 24 h. Cell survival was measured by CCK-8 assay, and morphological changes were monitored by time-lapse live cell imaging. The expression of receptor-interacting protein 1/3 (RIP1/3) and caspase 8 was assessed by westernblot, and the formation of necrosome (characterized by the assembly of RIP1/3 complex along with the dissociation of caspase 8) was examined by immunoprecipitation. Additionally, the production of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) was detected by using a ROS detection kit with an oxidation-sensitive probe (DCFH-DA).
Results: FOLE dose-dependently induced non-apoptotic, but programmed necroctic cell death (necroptosis) within 4-8 h after treatment. The assembly of RIP1/3 complex along with the dissociation of caspase 8 from RIP1 was observed in FOLE-treated cells. Moreover, FOLE-induced cell death was significantly alleviated by inhibiting RIP1, and was further aggravated by inhibiting caspase 8. In addition, prior to cell death the accumulation of intracellular ROS was significantly increased in FOLE-treated cells (increased by approximately 5-fold versus control, p < 0.001), which could be attenuated by inhibiting RIP1 (decreased by approximately 35% versus FOLE, p < 0.05).
Conclusions: FOLE induces RIP1-dependent and caspase 8-licensed necroptosis through overproduction of ROS in vitro. Our findings may provide novel insights into the clinical applications of FOLE during PN support.
Keywords: Caspase 8; Fish oil-derived lipid emulsion; IEC-6; Necroptosis; Parenteral nutrition; Reactive oxygen species; Receptor-interacting protein 1.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Feng Y, Barrett M, Hou Y, Yoon HK, Ochi T, Teitelbaum DH. Homeostasis alteration within small intestinal mucosa after acute enteral refeeding in total parenteral nutrition mouse model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016;310(4):G273–G284. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00335.2015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

