Prognostic Implication of BCR-ABL Fusion Transcript Variants in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) Treated with Imatinib. A First of Its Kind Study on CML Patients of Kashmir
- PMID: 29936718
- PMCID: PMC6103580
- DOI: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.6.1479
Prognostic Implication of BCR-ABL Fusion Transcript Variants in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) Treated with Imatinib. A First of Its Kind Study on CML Patients of Kashmir
Abstract
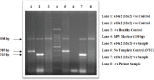
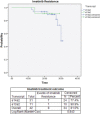
Background: The prognostic significance of the common BCR-ABL transcripts like e13a2 (b2a2) and e14a2 (b3a2) in Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has been reported from patients treated with different tyrosine kinase inhibitors but its impact on clinical response and overall survival remains still unexplored. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prognostic significance of different transcript types in a cohort of CML patients treated with imatinib. Methods: A total 42 confirmed cases of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) patients were recruited into our cohort study and a multiplex Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction technique (RT-PCR) was used to detect 3 main transcript types ‘e1a2’, ‘e13a2’, and ‘e14a2’ found in CML. Results: Only two types of transcripts e13a2 (b2a2) and e14a2 (b3a2) were detected in our CML patients and none had the e1a2 type. All the patients were RT-PCR positive for either e13a2 or e14a2 fusion transcript demonstrating 100% concordance with their Ph+ve cytogenetic status at baseline. TLC count (range of 201-600x103/μl) and platelet count (range of 201-900x103/μl) at baseline were found to be associated more with the e14a2 (b3a2) than the e13a2 (b2a2) transcript type (p-value: 0.001). The two transcripts found did not relate significantly towards sex, age-group or indicated spleen size ranges as well as percentage ranges of blast cells. Conclusion: We conclude that there is no overall prognostic implication of either the e13a2 or the e14a2 transcript type across the spectrum of indicated clinical parameters evaluated. Even the overall survival analysis of the two transcript types revealed no prognostic association whatsoever.
Keywords: BCR-ABL; chronic myeloid leukemia; imatinib; survival; RT-PCR.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures
Similar articles
-
The BCR-ABL1 transcript type influences response and outcome in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated frontline with imatinib.Am J Hematol. 2017 Aug;92(8):797-805. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24774. Epub 2017 May 30. Am J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28466557
-
Influence of BCR-ABL Transcript Type on Outcome in Patients With Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treated With Imatinib.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017 Nov;17(11):728-733. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.06.009. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017. PMID: 28822797 Review.
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia patients with the e13a2 BCR-ABL fusion transcript have inferior responses to imatinib compared to patients with the e14a2 transcript.Haematologica. 2009 Oct;94(10):1362-7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.009134. Epub 2009 Aug 27. Haematologica. 2009. PMID: 19713230 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct characteristics of e13a2 versus e14a2 BCR-ABL1 driven chronic myeloid leukemia under first-line therapy with imatinib.Haematologica. 2014 Sep;99(9):1441-7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.096537. Epub 2014 May 16. Haematologica. 2014. PMID: 24837466 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The impact of BCR-ABL1 transcript type on tyrosine kinase inhibitor responses and outcomes in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia.Cancer. 2018 Oct 1;124(19):3806-3818. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31408. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29694669
Cited by
-
Clinicopathological Variables and Outcome in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Associated With BCR-ABL1 Transcript Type and Body Weight: An Outcome of European LeukemiaNet Project.Cancer Control. 2021 Jan-Dec;28:10732748211038429. doi: 10.1177/10732748211038429. Cancer Control. 2021. PMID: 34789006 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights into the multifaceted roles of m6A-modified LncRNAs in cancers: biological functions and therapeutic applications.Biomark Res. 2023 Apr 17;11(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s40364-023-00484-7. Biomark Res. 2023. PMID: 37069649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: Incidence of BCR/ABL transcript and its correlation with presenting features, response to treatment, and survival.Leuk Res Rep. 2023 May 26;20:100373. doi: 10.1016/j.lrr.2023.100373. eCollection 2023. Leuk Res Rep. 2023. PMID: 37521582 Free PMC article.
-
Depleting long noncoding RNA HOTAIR attenuates chronic myelocytic leukemia progression by binding to DNA methyltransferase 1 and inhibiting PTEN gene promoter methylation.Cell Death Dis. 2021 May 3;12(5):440. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03637-4. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33941772 Free PMC article.
-
A decade of pyridine-containing heterocycles in US FDA approved drugs: a medicinal chemistry-based analysis.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Oct 10;16(1):12-36. doi: 10.1039/d4md00632a. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39493227 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arana-Trejo RM, Ruiz Sanchez E, Ignacio-Ibarra G, et al. BCR/ABL p210, p190 and p230 fusion genes in 250 Mexican patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) Clin Lab Haematol. 2002;24:145–50. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Neriah Y, Daley GQ, Mes-Masson AM, Witte ON, Baltimore D. The chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific P210 protein is the product of the bcr/abl hybrid gene. Science. 1986;233:212–14. - PubMed
-
- Bhutani M, Vora A, Kumar L, Kochupillai V. Lympho-hemopoietic malignancies in India. Med Oncol. 2002;19:141–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous