Development of murine bariatric surgery models: lessons learned
- PMID: 29937006
- PMCID: PMC6298430
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2018.04.022
Development of murine bariatric surgery models: lessons learned
Abstract
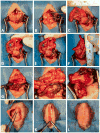
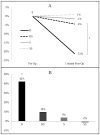
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) improves comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension and lowers the risk of obesity-related cancers. To better understand the physiologic and genetic influences of bariatric surgery, a reliable murine model is needed that can be extended to genetically engineered mice. Given the complexity of these procedures, few researchers have successfully implemented these techniques beyond larger rodent models. The purpose of our study was to develop a technically feasible and reproducible murine model for RYGB and sleeve gastrectomy (SG). Mice were converted to liquid diet perioperatively without fasting and housed in groups on raised wire platforms. SG involved significant reduction of stomach volume followed by multilayer repair of the gastrotomy. RYGB procedure consisted of side-to-side, functional end-to-side bowel anastomoses and exclusion of the stomach medial to the gastroesophageal junction. Sham surgeries consisted of enterotomies and gastrotomy followed by primary repair without resection or rerouting. Survival after incorporation of the aforementioned techniques was 100% in the SG group and 41% in the RYGB group at 1 mo after surgery. Only 26% of RYGB mortality was attributed to leak, obstruction, or stricture; the majority of postoperative mortality was due to stress, dumping, or malnutrition. Much of the survival challenge for this surgical model was related to perioperative husbandry, which is to be expected given their small stature and poor response to stress. Utilization of the perioperative and surgical techniques described will increase survival and feasibility of these technically challenging procedures, allowing for a better understanding of mechanisms to explain the beneficial effects of bariatric surgery.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Murine model; Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bae J, Shade J, Abraham A, et al. Effect of Mandatory Centers of Excellence Designation on Demographic Characteristics of Patients Who Undergo Bariatric Surgery. JAMA Surg. 2015;150(7):644–648. - PubMed
-
- Skolnik NS, Ryan DH. Pathophysiology, epidemiology, and assessment of obesity in adults. J Fam Pract. 2014;63(7 Suppl):S3–S10. - PubMed
-
- Lavie CJ, McAuley PA, Church TS, Milani RV, Blair SN. Obesity and cardiovascular diseases: implications regarding fitness, fatness, and severity in the obesity paradox. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(14):1345–1354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

