Disruption of GRIN2B Impairs Differentiation in Human Neurons
- PMID: 29937144
- PMCID: PMC6067152
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.05.018
Disruption of GRIN2B Impairs Differentiation in Human Neurons
Abstract
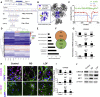
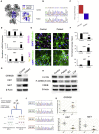
Heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in GRIN2B, a subunit of the NMDA receptor, cause intellectual disability and language impairment. We developed clonal models of GRIN2B deletion and loss-of-function mutations in a region coding for the glutamate binding domain in human cells and generated neurons from a patient harboring a missense mutation in the same domain. Transcriptome analysis revealed extensive increases in genes associated with cell proliferation and decreases in genes associated with neuron differentiation, a result supported by extensive protein analyses. Using electrophysiology and calcium imaging, we demonstrate that NMDA receptors are present on neural progenitor cells and that human mutations in GRIN2B can impair calcium influx and membrane depolarization even in a presumed undifferentiated cell state, highlighting an important role for non-synaptic NMDA receptors. It may be this function, in part, which underlies the neurological disease observed in patients with GRIN2B mutations.
Keywords: CRISPR; CRISPR-Cas9; GRIN2B; NMDA; NMDAR2B; NPCs; glutamate; iPSCs; neural stem cell; neurodevelopment.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
GRIN2B gain of function mutations are sensitive to radiprodil, a negative allosteric modulator of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Sep 1;123:322-331. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.05.017. Epub 2017 May 19. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28533163
-
Functional Evaluation of a Novel GRIN2B Missense Variant Associated with Epilepsy and Intellectual Disability.Neuroscience. 2023 Aug 21;526:107-120. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2023.06.018. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Neuroscience. 2023. PMID: 37385334
-
Expression and Functional Properties of NMDA and GABAA Receptors during Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Ventral Mesencephalic Neurons.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019 Mar;84(3):310-320. doi: 10.1134/S0006297919030131. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019. PMID: 31221069
-
Relationship between ketamine-induced developmental neurotoxicity and NMDA receptor-mediated calcium influx in neural stem cell-derived neurons.Neurotoxicology. 2017 May;60:254-259. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2016.04.015. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Neurotoxicology. 2017. PMID: 27132109 Review.
-
The Role of NMDA Receptors in Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation.Stem Cells Dev. 2017 Jun 1;26(11):798-807. doi: 10.1089/scd.2016.0325. Epub 2017 May 10. Stem Cells Dev. 2017. PMID: 28381110 Review.
Cited by
-
FOXG1 Dose in Brain Development.Front Pediatr. 2019 Nov 22;7:482. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00482. eCollection 2019. Front Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31824897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional Dysregulation and Impaired Neuronal Activity in FMR1 Knock-Out and Fragile X Patients' iPSC-Derived Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 5;24(19):14926. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914926. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834379 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Dysfunction by Mutations in GRIN2B: Influence of Triheteromeric NMDA Receptors on Gain-of-Function and Loss-of-Function Mutant Classification.Brain Sci. 2022 Jun 15;12(6):789. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12060789. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35741674 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping cortical malformations in patients with pathogenic variants in GRIN1 and GRIN2B.J Med Genet. 2023 Feb;60(2):183-192. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2021-107971. Epub 2022 Apr 7. J Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 35393335 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Brain Modulators in Neurodevelopment: Focus on Autism Spectrum Disorder and Associated Comorbidities.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 May 16;15(5):612. doi: 10.3390/ph15050612. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aamodt S.M., Constantine-Paton M. The role of neural activity in synaptic development and its implications for adult brain function. Adv. Neurol. 1999;79:133–144. - PubMed
-
- Adams D.R., Yuan H., Holyoak T., Arajs K.H., Hakimi P., Markello T.C., Wolfe L.A., Vilboux T., Burton B.K., Fajardo K.F. Three rare diseases in one Sib pair: RAI1, PCK1, GRIN2B mutations associated with Smith-Magenis syndrome, cytosolic PEPCK deficiency and NMDA receptor glutamate insensitivity. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014;113:161–170. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bading H., Ginty D.D., Greenberg M.E. Regulation of gene expression in hippocampal neurons by distinct calcium signaling pathways. Science. 1993;260:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Balazs R., Hack N., Jorgensen O.S. Stimulation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor has a trophic effect on differentiating cerebellar granule cells. Neurosci. Lett. 1988;87:80–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

