Apoptotic Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Malignancy of Glioblastoma Via Intercellular Transfer of Splicing Factors
- PMID: 29937354
- PMCID: PMC6048596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.05.012
Apoptotic Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Malignancy of Glioblastoma Via Intercellular Transfer of Splicing Factors
Abstract
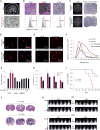
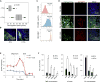
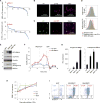
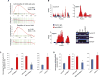
Aggressive cancers such as glioblastoma (GBM) contain intermingled apoptotic cells adjacent to proliferating tumor cells. Nonetheless, intercellular signaling between apoptotic and surviving cancer cells remain elusive. In this study, we demonstrate that apoptotic GBM cells paradoxically promote proliferation and therapy resistance of surviving tumor cells by secreting apoptotic extracellular vesicles (apoEVs) enriched with various components of spliceosomes. apoEVs alter RNA splicing in recipient cells, thereby promoting their therapy resistance and aggressive migratory phenotype. Mechanistically, we identified RBM11 as a representative splicing factor that is upregulated in tumors after therapy and shed in extracellular vesicles upon induction of apoptosis. Once internalized in recipient cells, exogenous RBM11 switches splicing of MDM4 and Cyclin D1 toward the expression of more oncogenic isoforms.
Keywords: alternative splicing; apoptosis; extracellular vesicles; glioblastoma; glioma; proneural-to-mesenchymal transition; spliceosome.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Bonnal S, Vigevani L, Valcárcel J. The spliceosome as a target of novel antitumour drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11:847–859. - PubMed
-
- Brat DJ, Castellano-Sanchez AA, Hunter SB, Pecot M, Cohen C, Hammond EH, Devi SN, Kaur B, Van Meir EG. Pseudopalisades in glioblastoma are hypoxic, express extracellular matrix proteases, and are formed by an actively migrating cell population. Cancer Res. 2004;64:920–927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

