Role of T-Helper 9 Cells in Chronic Hepatitis C-Infected Patients
- PMID: 29937515
- PMCID: PMC6071239
- DOI: 10.3390/v10070341
Role of T-Helper 9 Cells in Chronic Hepatitis C-Infected Patients
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus is a hepatotropic virus that is transmitted parenterally. Viral infections are usually associated with modulations of the immune cells, leading to enhanced viral survival and spreading, and accordingly, life-threatening complications. Recently, it has been proposed that a new subset of T-helper, named T-helper 9, is involved in the pathogenesis of different immunopathological conditions, such as allergies, tumors, and viral infections. Some studies reported a protective role, and others described a pathogenic potential for the T-helper 9 cells. Here, we present evidence that T-helper 9 cells are dynamically increased with increasing the pathogenic strategy for hepatitis C virus (HCV). Furthermore, viral clearance is associated with a decrease in T-helper 9. The increase in T-helper 9 was paralleled with an increase in its receptor expression. Taken together, our data suggest that T-helper 9 cells play an important role in the pathogenesis of HCV, and is directly associated with HCV-related complications.
Keywords: HCV-related complications; T-helper 9 cells; hepatitis C virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
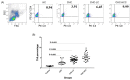
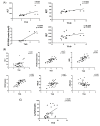
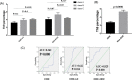
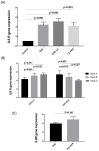
References
-
- Mehta M., Hetta H.F., Abdel-Hameed E.A., Rouster S.D., Hossain M., Mekky M.A., Khalil N.K., Mohamed W.A., El-Feky M.A., Ahmed S.H., et al. Association between il28b rs12979860 single nucleotide polymorphism and the frequency of colonic treg in chronically HCV-infected patients. Arch. Virol. 2016;161:3161–3169. doi: 10.1007/s00705-016-3015-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

