Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Associated with Internal Carotid Artery Dissection and Pseudoaneurysm
- PMID: 29937650
- PMCID: PMC5994847
- DOI: 10.4103/JETS.JETS_31_17
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Associated with Internal Carotid Artery Dissection and Pseudoaneurysm
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
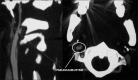
Figures

References
-
- Spanos K, Karathanos C, Stamoulis K, Giannoukas AD. Endovascular treatment of traumatic internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm. Injury. 2016;47:307–12. - PubMed
-
- Rathlev NK. Penetrating neck trauma: Mandatory versus selective exploration. J Emerg Med. 1990;8:75–8. - PubMed
-
- Wang A, Santarelli JG, Stiefel MF. Traumatic cervical internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in a child refractory to initial endovascular treatment: Case report and technical considerations. Childs Nerv Syst. 2016;32:2459–64. - PubMed
-
- Biffl WL, Moore EE, Offner PJ, Brega KE, Franciose RJ, Elliott JP, et al. Optimizing screening for blunt cerebrovascular injuries. Am J Surg. 1999;178:517–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

