Imaging assessment of profound sensorineural deafness with inner ear anatomical abnormalities
- PMID: 29937779
- PMCID: PMC6002563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joto.2015.07.005
Imaging assessment of profound sensorineural deafness with inner ear anatomical abnormalities
Abstract
Objective: To explore the value of a combined computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in evaluating profound sensorineural deafness patients before cochlear implant (CI) surgery.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 1012 cases of profound sensorineural deafness that received CI was performed.
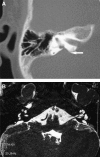
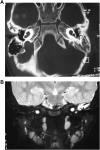
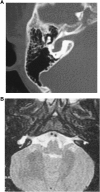
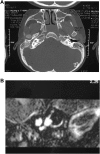
Results: A total of 96 cases were diagnosed with inner ear abnormalities including large vestibular aqueduct syndrome (LVAS, n = 61), Michel deformity (n = 3), cochlear incomplete partition I (n = 2), cochlear incomplete partition II (n = 6), cochlear hypoplasia with vestibular malformation (n = 3), cochlear ossification (n = 3), bilateral internal auditory canal obstruction (n = 5) and internal auditory canal stenosis (n = 2).
Conclusion: High resolution CT (HRCT) can display bony structures while MRI can image the membranous labyrinth in preoperative evaluation for cochlear implantation. The combination of these two modalities provides reliable anatomical information regarding the bony and membranous labyrinths, as well as the auditory nerve.
Keywords: Cochlea; Hearing loss; Multimodal imaging.
Figures





References
-
- Baek S.K., Chae S.W., Jung H.H. Congenital internal auditory canal stenosis. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2003;117:784. - PubMed
-
- Boston M., Halstead M., Meinzen-Derr J. The large vestibular aqueduct: a new definition based on audiologic and computed tomography correlation. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007;136:972–977. - PubMed
-
- Egelhoff J.C., Ball W.S., Towbin R.B. Dural ectasia as a cause of widening of the internal auditory canal in patients with neurofibromatosis. Pediatr. Radiol. 1989;17:79. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira T., Shayestehfar B., Lufkin R. Narrow, duplicated internal auditory canal. Neuroradiology. 2003;45(5):308–310. - PubMed
-
- Harnsberger . vol. 35–37. Amirsys Inc; Salt Lake City, Utah: 2003. pp. 62–70. (Temporal Bone Top 100 Diagnoses).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

