A Nomogram for Distinction and Potential Prediction of Liver Metastasis in Breast Cancer Patients
- PMID: 29937928
- PMCID: PMC6010683
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.24445
A Nomogram for Distinction and Potential Prediction of Liver Metastasis in Breast Cancer Patients
Abstract
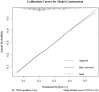
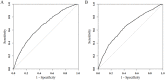
Liver metastasis from breast cancer has poor prognosis. We aimed at developing a reliable tool for making a distinction and prediction for liver metastasis in breast cancer patients, thus helping clinical diagnosis and treatment. In this study, totally 6238 patients from SEER database with known distant metastasis status and clinicopathologic variables were enrolled and divided randomly into training and validating groups. Logistic regression was used to screen variables and a nomogram was constructed. After multivariate logistic regression, sex, histology type, N stage, grade, age, ER, PR, HER2 status as significant variables for constructing the nomogram. The nomogram for distinguishing and predicting liver metastasis in breast cancer passed the calibration and validation steps and the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve of the training set and the validation set were 0.6602 and 0.6511 respectively. Our nomogram is a reliable and robust tool for the distinction and prediction of liver metastasis in breast cancer patients, thus helping better choose medical examinations and optimize therapeutic regimen under the cooperation among medical oncologists and surgeons.
Keywords: SEER; breast cancer; liver metastasis; nomogram.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



References
-
- Ferlay J SI, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F, v1.0 G. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013.
-
- DeSantis C, Siegel R, Bandi P, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:409–18. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Tabariès S, Siegel PM. Breast Cancer Liver Metastasis. In: Brodt P, editor. Liver Metastasis: Biology and Clinical Management. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands; 2011. p. 273-303.
-
- Ruiz A, Wicherts DA, Sebagh M, Giacchetti S, Castro-Benitez C, van Hillegersberg R. et al. Predictive Profile-Nomogram for Liver Resection for Breast Cancer Metastases: An Aggressive Approach with Promising Results. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24:535–45. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

