Metronomic combination of Vinorelbine and 5Fluorouracil is able to inhibit triple-negative breast cancer cells. Results from the proof-of-concept VICTOR-0 study
- PMID: 29937997
- PMCID: PMC6007943
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.25422
Metronomic combination of Vinorelbine and 5Fluorouracil is able to inhibit triple-negative breast cancer cells. Results from the proof-of-concept VICTOR-0 study
Abstract
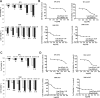
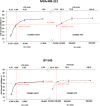
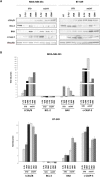
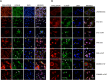
Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive neoplasia with median Overall Survival (OS) less than two years. Despite the availability of new drugs, the chance of survival of these patients did not increase. The combination of low doses of drugs in a metronomic schedule showed efficacy in clinical trials, exhibiting an anti-proliferative and anti-tumour activity. In Victor-2 study we recently evaluated a new metronomic combination (mCHT) of Capecitabine (CAPE) and Vinorelbine (VNR) in breast cancer patients showing a disease control rate with a median Progression-Free Survival (PFS) of 4.7 months in 28 TNBC patients. Here in Victor-0 study, we examined the effect of mCHT vs standard (STD) schedule of administration of different combinations of 5-Fluorouracil (5FU), the active metabolite of CAPE, and VNR in TNBC cell lines MDA-MB-231 and BT-549. A significant anti-proliferative activity was observed in cells treated with metronomic vs STD administration of 5FU or VNR alone. Combination of the two drugs showed an additive inhibitor effect on cell growth in both cell lines. Moreover, after exposure of cells to 5FU and VNR under mCHT or conventional schedule of administration we also observed a downregulation of chemoresistance factor Bcl-2, changes in pro-apoptotic protein Bax and in cleaved effector caspase-3 and increased expression of LC3A/B autophagy protein. Our results therefore suggest that molecular mechanisms implicated in apoptosis and autophagy as well as the cross-talk between these two forms of cell death in MDA-MB-231 and BT-549 cells treated with 5FU and VNR is dose- and schedule-dependent and provide some insights about the roles of autophagy and senescence in 5FU/VNR-induced cell death.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; LC3A/B; metronomic combination; triple-negative breast cancer; vinorelbine.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-targeting triple-negative breast cancer cells and endothelial cells by metronomic chemotherapy inhibits cell regrowth and migration via downregulation of the FAK/VEGFR2/VEGF axis and autophagy/apoptosis activation.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 30;12:998274. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.998274. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36531071 Free PMC article.
-
Metronomic chemotherapy (mCHT) in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients: results of the VICTOR-6 study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Dec;190(3):415-424. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06375-5. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34546500 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent bidirectional pharmacological effects of vinorelbine-based metronomic combination chemotherapy on tumor growth and metastasis and mechanisms in melanoma mouse model.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Feb;38(1):99-112. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12939. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37458143
-
Metronomics chemotherapy: time for computational decision support.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014 Sep;74(3):647-52. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2546-1. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25082520 Review.
-
Metronomic Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: The Future Is Now?Int J Breast Cancer. 2017;2017:1683060. doi: 10.1155/2017/1683060. Epub 2017 Dec 3. Int J Breast Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29333297 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Treating advanced breast cancer with metronomic chemotherapy: what is known, what is new and what is the future?Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Apr 23;12:2989-2997. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S189163. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31114242 Free PMC article.
-
Co-targeting triple-negative breast cancer cells and endothelial cells by metronomic chemotherapy inhibits cell regrowth and migration via downregulation of the FAK/VEGFR2/VEGF axis and autophagy/apoptosis activation.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 30;12:998274. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.998274. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36531071 Free PMC article.
-
Metronomic Chemotherapy for Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment: Clinical and Preclinical Data between Lights and Shadows.J Clin Med. 2022 Aug 12;11(16):4710. doi: 10.3390/jcm11164710. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36012949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Paradoxical Role of Cellular Senescence in Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 12;9:722205. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.722205. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34458273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senescence-Induced Chemoresistance in Triple Negative Breast Cancer and Evolution-Based Treatment Strategies.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 24;11:674354. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.674354. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34249714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schneider BP, Winer EP, Foulkes WD, Garber J, Perou CM, Richardson A, Sledge GW, Carey LA. Triple-negative breast cancer: risk factors to potential targets. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:8010–8. - PubMed
-
- Palma G, Frasci G, Chirico A, Esposito E, Siani C, Saturnino C, Arra C, Ciliberto G, Giordano A, D’Aiuto M. Triple negative breast cancer: looking for the missing link between biology and treatments. Oncotarget. 2015;6:26560–74. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5306 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Desidero T, Xu P, Man S, Bocci G, Kerbel RS. Potent efficacy of metronomic topotecan and pazopanib combination therapy in preclinical models of primary or late stage metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:42396–410. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6377 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fontana A, Falcone A, Derosa L, Di Desidero T, Danesi R, Bocci G. Metronomic chemotherapy for metastatic prostate cancer: A ‘young’concept for old patients? Drugs Aging. 2010;27:689–96. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

