[The preliminary study on biomechanical properties of four synthetic implants for reconstructive surgery of pelvic floor dysfunction]
- PMID: 29938949
- PMCID: PMC9935224
- DOI: 10.7507/1001-5515.201707071
[The preliminary study on biomechanical properties of four synthetic implants for reconstructive surgery of pelvic floor dysfunction]
Abstract
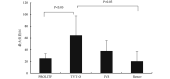
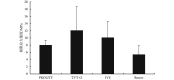
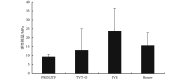
This study aimed to investigate biomechanical properties of synthetic implants for reconstructive surgery of pelvic floor dysfunction. In this dissertation, we chose four synthetic implants, i.e. total pelvic floor repair system (PROLIFT), gynecone TVT obtutator system (TVT-O), intra-vaginal sling placement device (IVS) and acellular dermal matrix (Renov), for tensile test respectively. The biomechanical properties of four synthetic implants were measured and analyzed using a material testing machine (Instron 4302 versatile material testing machine). The biomechanical parameters included ultimate stress strength, modulus of elasticity, maximum load and maximum elongation. The results showed that the maximum load of the four symthetic implants was TVT-O > IVS > PROLIFT > Renov, and the maximum load of TVT-O was significantly higher than PROLIFT and Renov ( P < 0.05). The ultimate stress strength was TVT-O > IVS > PROLIFT > Renov, with no significant differences among them ( P > 0.05). The maximum elongation of the four implants was TVT-O > PROLIFT > IVS > Renov, and the maximum elongation of TVT-O and PROLIFT were both significantly higher than Renov ( P < 0.05). The modulus of elasticity was IVS > Renov > TVT-O > PROLIFT, with no significant differences among them ( P > 0.05). Taken together, the present study demonstrates that the modulus of elasticity of IVS was the highest in the four synthetic implants; TVT-O had the highest mechanical strength; The maximum load, ultimate stress strength and maximum elongation of Renov were all the lowest; The mechanical properties of PROLIFT was the most stable, and its modulus of elasticity was the lowest in the four synthetic implants, which had good extensibility and elasticity. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the biomechanical properties of new pelvic reconstructive materials for the clinical pelvic reconstructive surgery.
为探讨盆底修复材料的生物力学特征,本试验选取用于女性盆底重建手术的 4 种盆底修复材料,分别是全盆底修复系统(PROLIFT)、经闭孔无张力阴道悬吊系统(TVT-O)、经阴道悬吊置入系统(IVS)和脱细胞异体真皮基质医用组织补片(Renov)。将 4 种盆底修复材料分别在 Instron4302 万能材料试验机上进行拉伸力学试验,记录极限应力强度、弹性模量、最大负荷和最大伸长量。结果显示:4 种盆底修复材料的最大负荷依次为 TVT-O > IVS > PROLIFT > Renov,TVT-O 最大负荷显著高于 PROLIFT和Renov( P < 0.05);极限应力强度依次为 TVT-O > IVS > PROLIFT > Renov,但 4 种材料组间比较差异无统计学意义( P > 0.05);最大伸长量依次为 TVT-O > PROLIFT > IVS > Renov,TVT-O 和 PROLIFT 的最大伸长量均显著高于 Renov( P < 0.05);弹性模量依次为 IVS > Renov > TVT-O > PROLIFT,但 4 种材料组间比较差异无统计学意义( P > 0.05)。可见,4 种盆底修复材料中,IVS 的弹性模量最高;TVT-O 的力学强度最高;Renov 的最大负荷、极限应力强度以及最大伸长量均最低;PROLIFT 材料的力学性能最稳定,弹性模量最低,具有良好的延展性和弹性。因此,综合临床盆底重建手术的实际需要,在开发新型盆底修复材料时应注重其生物力学性能的考量。.
Keywords: biomechanics; maximum elongation; maximum load; modulus of elasticity; reconstructive surgery of pelvic floor dysfunction; synthetic implants; ultimate stress strength.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Elongation of textile pelvic floor implants under load is related to complete loss of effective porosity, thereby favoring incorporation in scar plates.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014 Apr;102(4):1079-84. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34767. Epub 2013 Jun 11. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014. PMID: 23625516
-
[New options in reconstructive pelvic floor surgery and surgery in urogynecology].Ceska Gynekol. 2006 Dec;71(6):455-63. Ceska Gynekol. 2006. PMID: 17236404 Review. Czech.
-
[Study on modified Prolift for pelvic floor reconstruction in the prevention of stress urinary incontinence].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Jul;47(7):505-9. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23141160 Chinese.
-
Tissue reactions of 5 sling materials and tissue material detachment strength of 4 synthetic mesh materials in a rabbit model.J Urol. 2005 Nov;174(5):2037-40. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000176478.17749.07. J Urol. 2005. PMID: 16217389
-
Tension-free vaginal tape and percutaneous vaginal tape sling procedures.Tech Urol. 2001 Jun;7(2):90-100. Tech Urol. 2001. PMID: 11384000 Review.
References
-
- Morgan J E A sling operation, using Marlex polypropylene mesh, for treatment of recurrent stress incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970;106(3):369–377. - PubMed
-
- Stanton S L, Brindley G S, Holmes D M Silastic sling for urethral sphincter incompetence in women. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1985;92(7):747–750. - PubMed
-
- Iosif C S Abdominal sacral colpopexy with use of synthetic mesh. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1993;72(3):214–217. - PubMed
-
- Cervigni M, Natale F The use of synthetics in the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse. Curr Opin Urol. 2001;11(4):429–435. - PubMed
-
- Ridgeway B, Chen C C, Paraiso M F The use of synthetic mesh in pelvic reconstructive surgery. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2008;51(1):136–152. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
