Cluster randomized trial of the classroom SCERTS intervention for elementary students with autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 29939056
- PMCID: PMC6457665
- DOI: 10.1037/ccp0000314
Cluster randomized trial of the classroom SCERTS intervention for elementary students with autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
Objective: This cluster randomized trial (CRT) evaluated the efficacy of the Classroom Social, Communication, Emotional Regulation, and Transactional Support (SCERTS) Intervention (CSI) compared with usual school-based education with autism training modules (ATM).
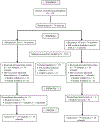
Method: Sixty schools with 197 students with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in 129 classrooms were randomly assigned to CSI or ATM. Mean student age was 6.79 years (SD 1.05) and 81.2% were male. CSI teachers were trained on the model and provided coaching throughout the school year to assist with implementation. A CRT, with students nested within general and special education classrooms nested within schools, was used to evaluate student outcomes.
Results: The CSI group showed significantly better outcomes than the ATM group on observed measures of classroom active engagement with respect to social interaction. The CSI group also had significantly better outcomes on measures of adaptive communication, social skills, and executive functioning with Cohen's d effect sizes ranging from 0.31 to 0.45.
Conclusion: These findings support the preliminary efficacy of CSI, a classroom-based, teacher-implemented intervention for improving active engagement, adaptive communication, social skills, executive functioning, and problem behavior within a heterogeneous sample of students with ASD. This makes a significant contribution to the literature by demonstrating efficacy of a classroom-based teacher-implemented intervention with a heterogeneous group of students with ASD using both observed and reported measures. (PsycINFO Database Record
(c) 2018 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Student-Teacher Relationships for Young Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Risk and Protective Factors.J Autism Dev Disord. 2016 Dec;46(12):3653-3666. doi: 10.1007/s10803-016-2915-1. J Autism Dev Disord. 2016. PMID: 27638649
-
Student-teacher relationships of children with autism spectrum disorder: Distinct contributions of language domains.Res Dev Disabil. 2019 Jun;89:94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Apr 6. Res Dev Disabil. 2019. PMID: 30959432 Free PMC article.
-
Student Engagement in the Classroom: The Impact of Classroom, Teacher, and Student Factors.J Autism Dev Disord. 2015 Aug;45(8):2392-410. doi: 10.1007/s10803-015-2406-9. J Autism Dev Disord. 2015. PMID: 25733160
-
Fostering Communication in Elementary School Children on the Autism Spectrum Who Are Minimally Verbal.Semin Speech Lang. 2018 Apr;39(2):103-113. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1627482. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Semin Speech Lang. 2018. PMID: 29558766 Review.
-
A systematic review of school-based interventions targeting social communication behaviors for students with autism.Autism. 2019 Feb;23(2):274-286. doi: 10.1177/1362361317753564. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Autism. 2019. PMID: 29382208
Cited by
-
Lost in Transition: Delayed Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder Following Early Migration.Cureus. 2025 Apr 24;17(4):e82883. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82883. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40416142 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Preschool Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Trial to Evaluate a Learning Style Profile Intervention Program in China.Front Pediatr. 2022 Mar 16;10:831621. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.831621. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35372141 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Teacher Language Within General and Special Education Classrooms Serving Elementary Students with Autism.J Autism Dev Disord. 2022 May;52(5):2284-2299. doi: 10.1007/s10803-021-05115-4. Epub 2021 Jun 9. J Autism Dev Disord. 2022. PMID: 34106392 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility and acceptability of a low-resource-intensive, transdiagnostic intervention for children with social-communication challenges in early childhood education settings.Autism. 2024 Mar;28(3):587-599. doi: 10.1177/13623613231179289. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Autism. 2024. PMID: 37291971 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Life Skills Training and Executive Function Strategies in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder in Qatar: A Pilot Study of a Randomized Controlled Trial.Cureus. 2024 Jan 23;16(1):e52809. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52809. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38264179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldred C, Green J, & Adams C (2004). A new social communication intervention for children with autism: Pilot randomised controlled treatment study suggesting effectiveness. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 45, 1420–1430. 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.00338.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., text rev.). Washington, DC: Author.
-
- Arick JR, Loos L, Falco R, & Krug DA (2004). The STAR Program: Strategies for teaching based on autism research, Levels I, II, & III. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.
-
- Baio J, Wiggins L, Christensen DL, Maenner MJ, Daniels J, Warren Z, … Dowling NF (2018). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years – Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 Sites, United States, 2014. MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 67, 1–23. 10.15585/mmwr.ss6706a1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, & Hochberg Y (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate – a new and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B, Methodological, 57, 289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous