The COPII cargo adapter SEC24C is essential for neuronal homeostasis
- PMID: 29939162
- PMCID: PMC6063503
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI98194
The COPII cargo adapter SEC24C is essential for neuronal homeostasis
Abstract
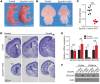
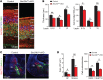
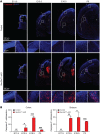
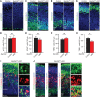
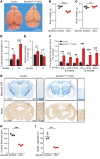
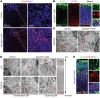
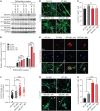
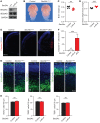
SEC24 family members are components of the coat protein complex II (COPII) machinery that interact directly with cargo or with other adapters to ensure proper sorting of secretory cargo into COPII vesicles. SEC24C is 1 of 4 mammalian SEC24 paralogs (SEC24A-D), which segregate into 2 subfamilies on the basis of sequence homology (SEC24A/SEC24B and SEC24C/SEC24D). Here, we demonstrate that postmitotic neurons, unlike professional secretory cells in other tissues, are exquisitely sensitive to loss of SEC24C. Conditional KO of Sec24c in neural progenitors during embryogenesis caused perinatal mortality and microcephaly, with activation of the unfolded protein response and apoptotic cell death of postmitotic neurons in the murine cerebral cortex. The cell-autonomous function of SEC24C in postmitotic neurons was further highlighted by the loss of cell viability caused by disrupting Sec24c expression in forebrain neurons of mice postnatally and in differentiated neurons derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. The neuronal cell death associated with Sec24c deficiency was rescued in knockin mice expressing Sec24d in place of Sec24c. These data suggest that SEC24C is a major cargo adapter for COPII-dependent transport in postmitotic neurons in developing and adult brains and that its functions overlap at least partially with those of SEC24D in mammals.
Keywords: Cell stress; Development; Neurodegeneration; Neurodevelopment; Neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

