Quantifying Microglia Morphology from Photomicrographs of Immunohistochemistry Prepared Tissue Using ImageJ
- PMID: 29939190
- PMCID: PMC6103256
- DOI: 10.3791/57648
Quantifying Microglia Morphology from Photomicrographs of Immunohistochemistry Prepared Tissue Using ImageJ
Abstract
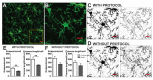
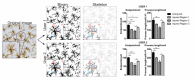
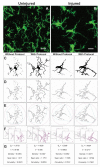
Microglia are brain phagocytes that participate in brain homeostasis and continuously survey their environment for dysfunction, injury, and disease. As the first responders, microglia have important functions to mitigate neuron and glia dysfunction, and in this process, they undergo a broad range of morphologic changes. Microglia morphologies can be categorized descriptively or, alternatively, can be quantified as a continuous variable for parameters such as cell ramification, complexity, and shape. While methods for quantifying microglia are applied to single cells, few techniques apply to multiple microglia in an entire photomicrograph. The purpose of this method is to quantify multiple and single cells using readily available ImageJ protocols. This protocol is a summary of the steps and ImageJ plugins recommended to convert fluorescence and bright-field photomicrographs into representative binary and skeletonized images and to analyze them using software plugins AnalyzeSkeleton (2D/3D) and FracLac for morphology data collection. The outputs of these plugins summarize cell morphology in terms of process endpoints, junctions, and length as well as complexity, cell shape, and size descriptors. The skeleton analysis protocol described herein is well suited for a regional analysis of multiple microglia within an entire photomicrograph or region of interest (ROI) whereas FracLac provides a complementary individual cell analysis. Combined, the protocol provides an objective, sensitive, and comprehensive assessment tool that can be used to stratify between diverse microglia morphologies present in the healthy and injured brain.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials