Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices
- PMID: 29939980
- PMCID: PMC5837403
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.rr6701a1
Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices
Abstract
HEPATITIS B VIRUS (HBV) IS TRANSMITTED VIA BLOOD OR SEXUAL CONTACT. PERSONS WITH CHRONIC HBV INFECTION ARE AT INCREASED RISK FOR CIRRHOSIS AND LIVER CANCER AND REQUIRE MEDICAL CARE. THIS REPORT UPDATES AND SUMMARIZES PREVIOUSLY PUBLISHED RECOMMENDATIONS FROM THE ADVISORY COMMITTEE ON IMMUNIZATION PRACTICES (ACIP) AND CDC REGARDING THE PREVENTION OF HBV INFECTION IN THE UNITED STATES. ACIP RECOMMENDS TESTING ALL PREGNANT WOMEN FOR HEPATITIS B SURFACE ANTIGEN (HBSAG), AND TESTING HBSAG-POSITIVE PREGNANT WOMEN FOR HEPATITIS B VIRUS DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID (HBV DNA); ADMINISTRATION OF HEPB VACCINE AND HEPATITIS B IMMUNE GLOBULIN (HBIG) FOR INFANTS BORN TO HBV-INFECTED WOMEN WITHIN 12 HOURS OF BIRTH, FOLLOWED BY COMPLETION OF THE VACCINE SERIES AND POSTVACCINATION SEROLOGIC TESTING; UNIVERSAL HEPATITIS B VACCINATION WITHIN 24 HOURS OF BIRTH, FOLLOWED BY COMPLETION OF THE VACCINE SERIES; AND VACCINATION OF CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS AGED <19 YEARS WHO HAVE NOT BEEN VACCINATED PREVIOUSLY. ACIP RECOMMENDS VACCINATION OF ADULTS AT RISK FOR HBV INFECTION, INCLUDING UNIVERSAL VACCINATION OF ADULTS IN SETTINGS IN WHICH A HIGH PROPORTION HAVE RISK FACTORS FOR HBV INFECTION AND VACCINATION OF ADULTS REQUESTING PROTECTION FROM HBV WITHOUT ACKNOWLEDGMENT OF A SPECIFIC RISK FACTOR. THESE RECOMMENDATIONS ALSO PROVIDE CDC GUIDANCE FOR POSTEXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS FOLLOWING OCCUPATIONAL AND OTHER EXPOSURES. THIS REPORT ALSO BRIEFLY SUMMARIZES PREVIOUSLY PUBLISHED AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OF LIVER DISEASEST GUIDELINES FOR MATERNAL ANTIVIRAL THERAPY TO REDUCE PERINATAL HBV TRANSMISSION.
Conflict of interest statement
The 2016–2017 ACIP Hepatitis Vaccines Work Group members wish to disclose that they have no financial or competing interests with the manufacturers of commercial products or suppliers of commercial services related to hepatitis B (HepB) vaccines. Content will not include any discussion of the unlabeled use of a product or a product under investigational use, with the following exceptions: use of Pediarix vaccine for infants born to hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)–positive mothers or mothers with an unknown HBsAg status to complete the vaccine series after receipt of a birth dose of single-antigen HepB vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG); alternate 3-dose vaccine administration schedules heeding to minimum intervals of 4 weeks between the first and second dose, 8 weeks between the second and third dose, and 16 weeks between the first and third dose; modified dosing regimens (e.g., doubling of standard dose and administration of additional doses) in certain circumstances (e.g., for persons with immunocompromising conditions); and antiviral therapy during pregnancy for the prevention of perinatal hepatitis B virus (HBV) transmission.
Figures

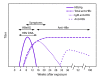
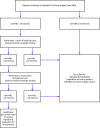
References
-
- CDC. Updated U.S. Public Health Service guidelines for the management of occupational exposures to HBV, HCV, and HIV and recommendations for postexposure prophylaxis. MMWR Recomm Rep 2001;50(No. RR-11):1–52. - PubMed
-
- Preboth M. PHS guidelines for management of occupational exposure to HBV, HCV and HIV: management of occupational blood exposures. Am Fam Physician 2001;64:2012–4. - PubMed
-
- CDC. Viral hepatitis—statistics and surveillance. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2017. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
