Overexpression of neuronal RNA-binding protein HuD increases reward induced reinstatement of an instrumental response
- PMID: 29940328
- PMCID: PMC6368978
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.06.038
Overexpression of neuronal RNA-binding protein HuD increases reward induced reinstatement of an instrumental response
Abstract
The neuronal RNA-binding protein HuD is involved in synaptic plasticity and the molecular mechanisms of learning and memory. Previously, we have shown that HuD is upregulated after both spatial and addiction-associated forms of learning, such as conditioned place preference. However, what role HuD plays in non-drug dependent learning and memory is not fully understood. In order to elucidate the role that HuD plays in non-drug appetitive behavior, we assessed mice over-expressing HuD (HuDOE) throughout the forebrain on the acquisition of an instrumental response for a non-sucrose food reward utilizing a touch-screen paradigm. Next, we examined whether HuD level would alter the extinction or reward-induced reinstatement of responding. We found that HuDOE acquired and extinguished the instrumental response at rates similar to control littermates with no significant alterations in secondary measures of motor behavior or motivation. However, HuDOE reinstated their responding for food reward at rates significantly higher than control animals after a brief presentation of reward. These results suggest that HuD positively regulates the reinstatement of natural reward seeking and supports the role of HuD in forms of learning and memory associated with seeking of appetitive rewards.
Keywords: HuD; Post-transcriptional regulation; RNA binding protein; Reward seeking.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
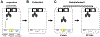
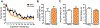
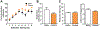
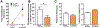
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

